Delving into the microscopic world of DNA, the very blueprint of life, can feel like embarking on a fascinating scientific adventure. To truly understand how organisms function and pass on their traits, grasping the intricate details of DNA structure and replication is paramount. That’s where a well-crafted “DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet” can be an invaluable tool. These worksheets typically provide a comprehensive overview, ranging from the fundamental components of DNA (nucleotides, sugars, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases) to the complex process by which DNA duplicates itself with remarkable fidelity. They offer a structured learning approach, often combining visual aids, interactive exercises, and challenging questions to solidify understanding.
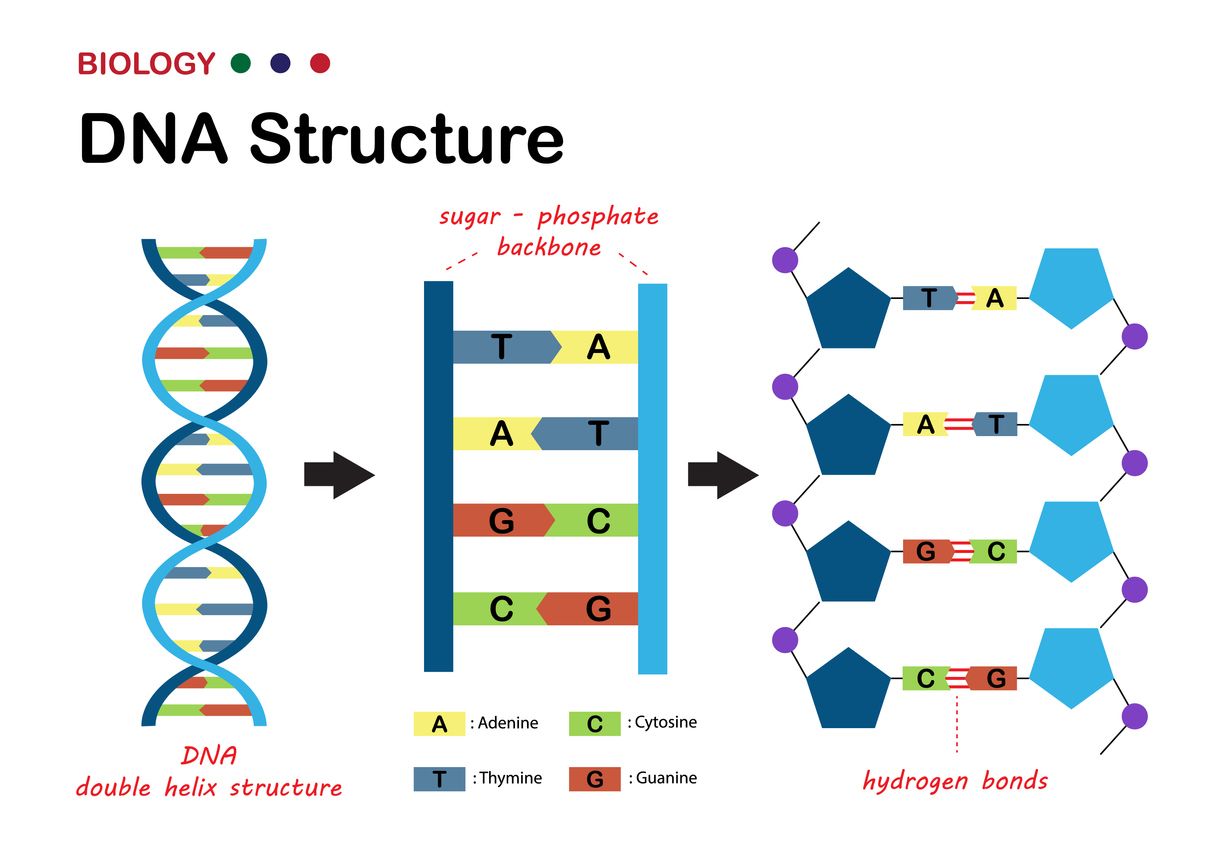
DNA structure worksheets frequently begin with identifying the key building blocks of a nucleotide: deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). They emphasize the double helix model proposed by Watson and Crick, highlighting the antiparallel arrangement of the two DNA strands and the specific base pairing rules (A with T, and C with G). Understanding these relationships is crucial for predicting DNA sequences and comprehending how genetic information is encoded. Worksheets may ask students to construct DNA models, label diagrams, or answer questions about the relative proportions of different bases within a DNA molecule based on Chargaff’s rules.
Moving beyond structure, DNA replication worksheets explore the enzymatic machinery involved in duplicating the DNA molecule. These worksheets often feature diagrams illustrating the steps of replication, including the role of enzymes like helicase (unzipping the DNA), DNA polymerase (synthesizing new strands), ligase (joining DNA fragments), and primase (initiating replication). Understanding the concepts of leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragments, and the directionality of DNA synthesis (5′ to 3′) is critical. Students might be asked to fill in missing bases in a replicating DNA sequence, identify the function of specific enzymes, or describe the steps involved in proofreading and error correction during replication. These activities help students to appreciate the precision and complexity of the replication process, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Successfully completing a DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet requires more than just memorization; it demands a conceptual understanding of the underlying principles. It pushes learners to actively engage with the material, analyze diagrams, solve problems, and explain processes in their own words. This active learning approach is far more effective than passively reading a textbook and dramatically improves retention of the information. Moreover, mastering the content covered in these worksheets lays a solid foundation for tackling more advanced topics in molecular biology, genetics, and biotechnology. So, embrace the challenge, dive into the world of DNA, and unlock the secrets of life one worksheet at a time!
DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answers
Please note: The following answers are examples. The specific questions on your worksheet may differ, so adapt these accordingly.
Part 1: DNA Structure
- Question 1: What are the three components of a nucleotide?
- Answer: Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- Question 2: Name the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA.
- Answer: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T).
- Question 3: Which bases pair together in DNA?
- Answer: Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
- Question 4: Describe the structure of the DNA double helix.
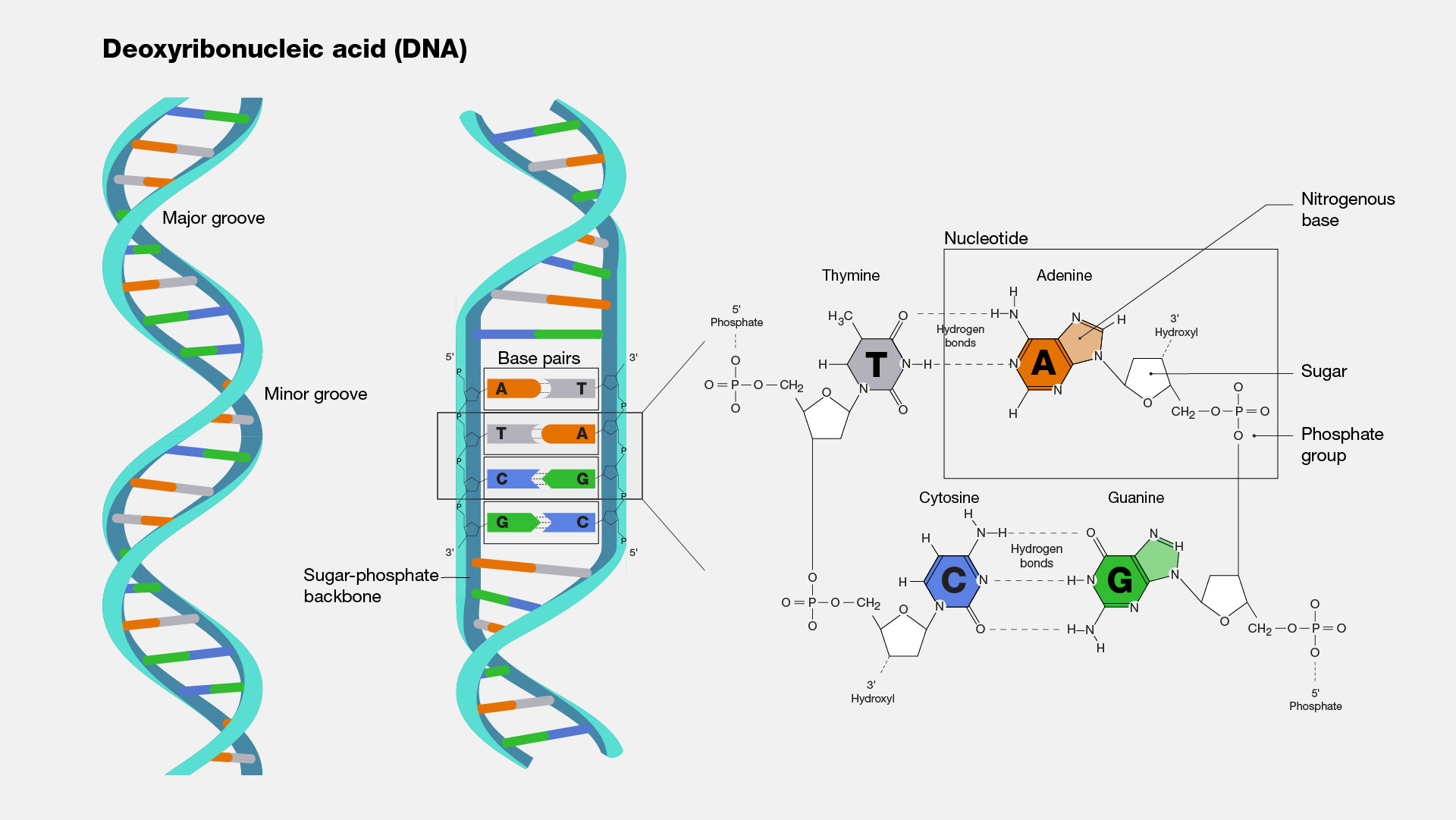
- Answer: Two antiparallel strands of nucleotides twisted around each other, forming a double helix. The sugar-phosphate backbone forms the outside, and the nitrogenous bases pair in the middle, held together by hydrogen bonds.
- Question 5: What does “antiparallel” mean in the context of DNA?
- Answer: It means that the two DNA strands run in opposite directions. One strand runs from 5′ to 3′, and the other strand runs from 3′ to 5′.
Part 2: DNA Replication
- Question 1: What is the purpose of DNA replication?
- Answer: To create an exact copy of the DNA molecule, ensuring that each new cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions.
- Question 2: What enzyme unwinds the DNA double helix?
- Answer: Helicase.
- Question 3: What enzyme adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand?
- Answer: DNA polymerase.
- Question 4: Explain the difference between the leading and lagging strands.
- Answer: The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5′ to 3′ direction, following the replication fork. The lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in short fragments (Okazaki fragments) also in the 5′ to 3′ direction, but away from the replication fork.
- Question 5: What are Okazaki fragments?
- Answer: Short fragments of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
- Question 6: What enzyme joins Okazaki fragments together?
- Answer: DNA ligase.
- Question 7: Why is DNA replication considered semi-conservative?
- Answer: Because each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
If you are looking for DNA Definition and Structure you’ve visit to the right place. We have 20 Pictures about DNA Definition and Structure like DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation, DNA Structure | Visual.ly and also Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Struktur, Fungsi, dan Kelainan DNA. Here it is:
DNA Definition And Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-476980521-56a134e65f9b58b7d0bd059b.jpg)
www.thoughtco.com
Digital Illustration Of A Dna

www.setaswall.com
DNA Structure | Visual.ly

visual.ly
What Does DNA Stand For, And How Does It Work? | Extremetech

www.extremetech.com
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model

alevelbiology.co.uk
What Is DNA? | Live Science

www.livescience.com
Colorful Human DNA Strand Surrounded, DNA Structure, 22379220 Stock
www.vecteezy.com
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Struktur, Fungsi, Dan Kelainan DNA
www.haibunda.com
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model

alevelbiology.co.uk
DNA Facts And Information

www.nationalgeographic.com
DNA – Definition, Function, Structure And Discovery | Biology Dictionary

biologydictionary.net
DNA | Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure

www.britannica.com
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
www.genome.gov
DNA Structure Model On White Stock Photo – Alamy

www.alamy.com
DNA | Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure

www.britannica.com
DNA Structure Isolated Background 3d Illustration 18871969 PNG

www.vecteezy.com
3d Structure Of Dna Model

ar.inspiredpencil.com
What Is DNA? – Definition, Structure, Types, Functions – GeeksforGeeks

www.geeksforgeeks.org
DNA: Definition, Structure And Functions | Healthtian

healthtian.com
DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, And Mutation
/3-D_DNA-56a09ae45f9b58eba4b20266.jpg)
www.thoughtco.com
Digital illustration of a dna. What does dna stand for, and how does it work?. dna structure
