Lewis structures, also known as electron dot diagrams, are powerful tools in chemistry for visualizing the bonding within molecules and polyatomic ions. They provide a simple, yet effective way to represent the arrangement of valence electrons around atoms and the bonds formed between them. Mastering the ability to draw and interpret Lewis structures is fundamental to understanding molecular geometry, polarity, reactivity, and many other chemical concepts.
This post is designed to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding Lewis structures, along with a practice worksheet and its corresponding answers. By working through the examples, you’ll reinforce your knowledge of the rules and steps involved in constructing these diagrams. So, grab a pencil, paper, and your periodic table, and let’s dive in!
Understanding the Rules of Lewis Structures
Before we jump into the worksheet, let’s briefly review the key principles behind constructing Lewis structures:
- Count Valence Electrons: The first step is to determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. Remember that valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and they are the ones involved in chemical bonding. Use the periodic table to determine the number of valence electrons for each atom in the molecule or ion, and then add them up. For ions, add electrons for negative charges and subtract electrons for positive charges.
- Determine the Central Atom: The central atom is typically the least electronegative element (excluding hydrogen, which is *always* terminal). Carbon is a common central atom. If there are multiple atoms with similar electronegativity, the one present in the smallest quantity usually takes the central position.
- Form Single Bonds: Connect the central atom to the surrounding atoms (terminal atoms) with single bonds. Each single bond represents a shared pair of electrons.
- Satisfy the Octet Rule: Distribute the remaining valence electrons as lone pairs around the terminal atoms to satisfy the octet rule (each atom should have eight electrons around it). Hydrogen is an exception; it only needs two electrons (duet rule).
- Place Remaining Electrons on Central Atom: After satisfying the octets of the terminal atoms, place any remaining valence electrons as lone pairs on the central atom.
- Form Multiple Bonds: If the central atom does not have an octet after all the valence electrons have been distributed, form multiple bonds (double or triple bonds) by sharing lone pairs from the terminal atoms with the central atom until the central atom has an octet.
Lewis Structures Worksheet
Now that we’ve refreshed our understanding of the rules, let’s put them into practice. Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecules and ions:
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrate Ion (NO3–)
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
- Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Ozone (O3)
- Formaldehyde (CH2O)
Check Your Answers!
Below you’ll find the correct Lewis structures for each of the molecules and ions listed above. Compare your work with the answers provided to identify any areas where you may need further practice. Remember to pay attention to the number of valence electrons, the central atom, the octet rule, and the placement of lone pairs and multiple bonds.
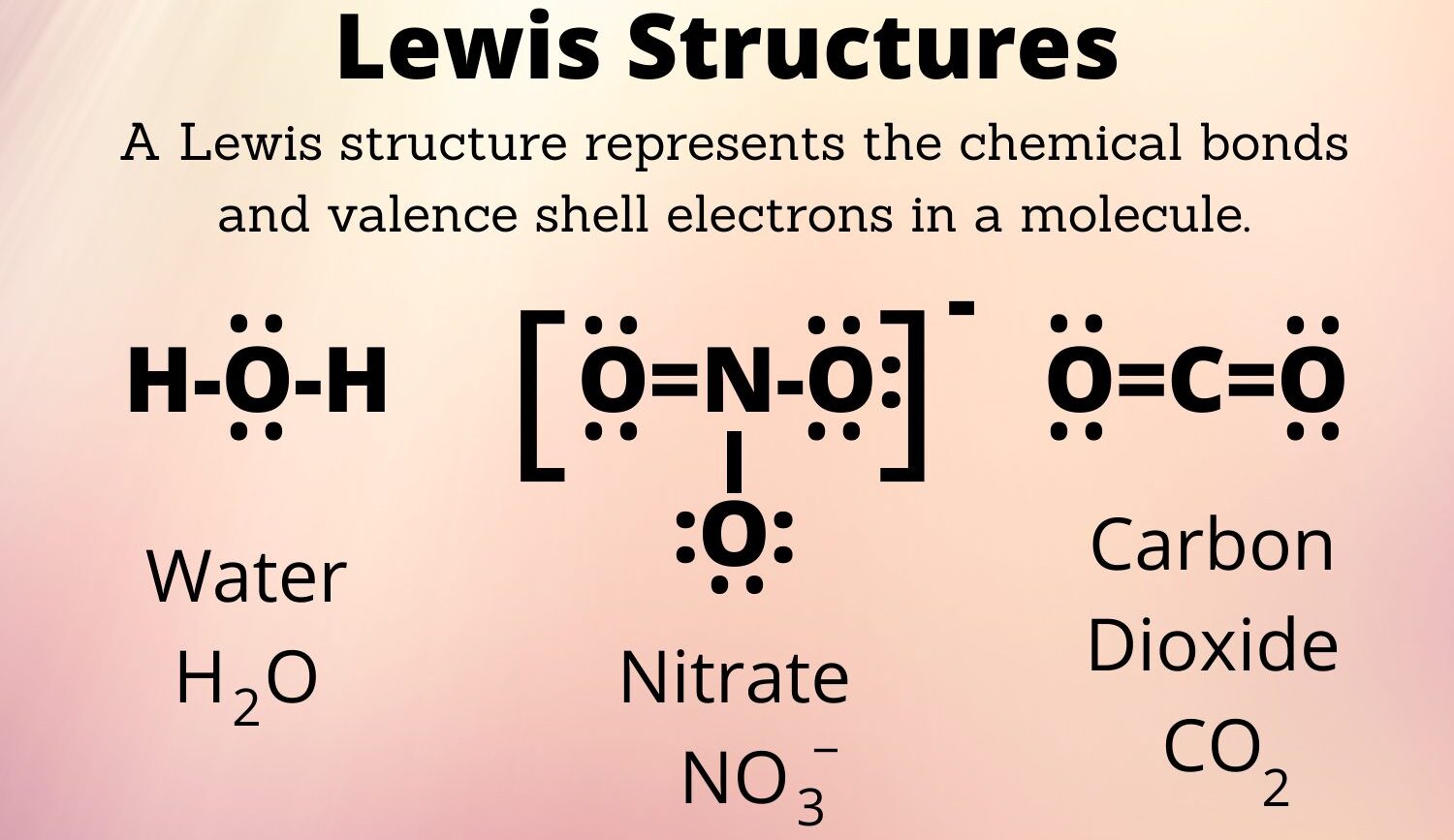
- 1. Water (H2O)
- Total Valence Electrons: 6 (O) + 1 (H) * 2 = 8
- Central Atom: O
- Structure: H-O-H with two lone pairs on O
- Total Valence Electrons: 4 (C) + 6 (O) * 2 = 16
- Central Atom: C
- Structure: O=C=O
- Total Valence Electrons: 5 (N) + 1 (H) * 3 = 8
- Central Atom: N
- Structure: H-N-H with one lone pair on N and each H singly bonded
- Total Valence Electrons: 4 (C) + 1 (H) * 4 = 8
- Central Atom: C
- Structure: C with four single bonds to H
- Total Valence Electrons: 5 (N) + 6 (O) * 3 + 1 (charge) = 24
- Central Atom: N
- Structure: N singly bonded to two O atoms each with 3 lone pairs, N doubly bonded to one O with 2 lone pairs; brackets with a -1 charge. Resonance structures possible.
- Total Valence Electrons: 6 (S) + 6 (O) * 2 = 18
- Central Atom: S
- Structure: O=S-O with a lone pair on S and resonance structures exist; terminal oxygen with single bond contains three lone pairs, oxygen with double bond contains two lone pairs.
- Total Valence Electrons: 1 (H) + 4 (C) + 5 (N) = 10
- Central Atom: C
- Structure: H-C≡N
- Total Valence Electrons: 4 (C) + 6 (O) = 10
- Structure: C≡O with one lone pair on each C and O.
- Total Valence Electrons: 6 (O) * 3 = 18
- Structure: O=O-O with one lone pair on central O. Resonance structures possible. Oxygen single bonded to central O has 3 lone pairs, oxygen double bonded to central oxygen has two lone pairs.
- Total Valence Electrons: 4 (C) + 1 (H) * 2 + 6 (O) = 12
- Structure: H-C-H with C double bonded to O. Oxygen has two lone pairs.
By working through these examples, you should have a much better understanding of how to draw Lewis structures. Keep practicing, and you’ll be creating these diagrams with confidence in no time!
If you are looking for Lewis Structure of PCl5? [with free study guide and video] you’ve visit to the right web. We have 20 Pics about Lewis Structure of PCl5? [with free study guide and video] like Structure de Lewis : définition et explications – AquaPortail, Lewis Dot Structure: Definition, Examples, and Drawing and also F2O Lewis Structure: How to Draw the Lewis Structure for F2O. Here you go:
Lewis Structure Of PCl5? [with Free Study Guide And Video]
![Lewis Structure of PCl5? [with free study guide and video]](https://www.aceorganicchem.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/PCl5-Lewis-puzzle-.jpg)
www.aceorganicchem.com
In The Space Below Draw A Reasonable Lewis Electron D – Vrogue.co
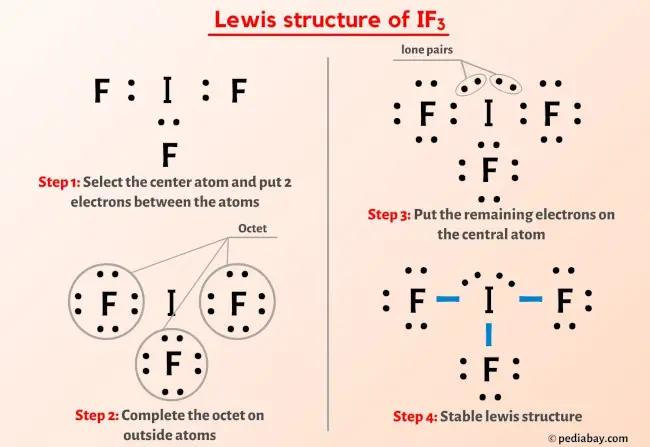
www.vrogue.co
HOCl Lewis Structure: How To Draw Lewis Dot Structure – YouTube

www.youtube.com
Lewis Dot Structure: Definition, Examples, And Drawing

www.chemistrylearner.com
THS-Quimica: Estructuras De Lewis De Los Elementos | UTN-FRRQ
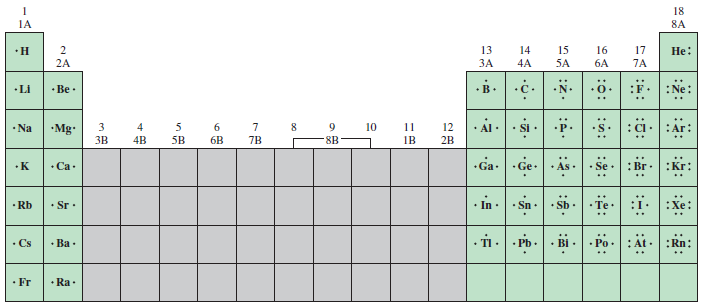
frrq.cvg.utn.edu.ar
The Lewis Structures Of C2H4O [with Free Study Guide And Video]
![The Lewis Structures of C2H4O [with free study guide and video]](https://www.aceorganicchem.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/acetaldeyde-step-method.jpg)
biochemhelp.com
¿Cuáles Son Las Aportaciones Del Trabajo De Lewis? – Nueva Escuela
nuevaescuelamexicana.sep.gob.mx
Estructuras De Lewis De óxidos, Oxácidos Y Sus Aniones – TRIPLENLACE

triplenlace.com
Hướng Dẫn Vẽ So2 Lewis Structure đơn Giản Và Chi Tiết Nhất
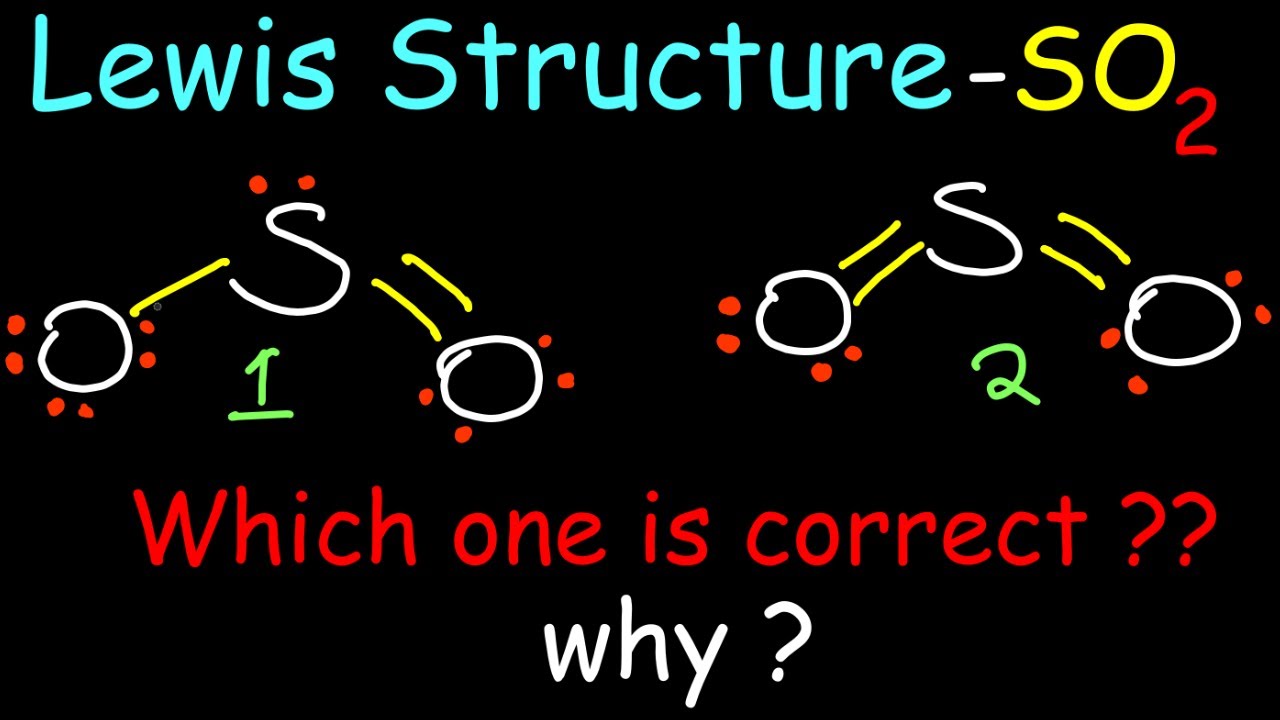
xaydungso.vn
25 Unbelievable Facts About Ramsey Lewis – Facts.net
facts.net
Lewis About Life

ar.inspiredpencil.com
David Coulthard's Theory On Lewis Hamilton's Mercedes Contract Delay

www.planetf1.com
Structure De Lewis : Définition Et Explications – AquaPortail

www.aquaportail.com
Lewis Symbols And Structures | Chemistry I | | Course Hero
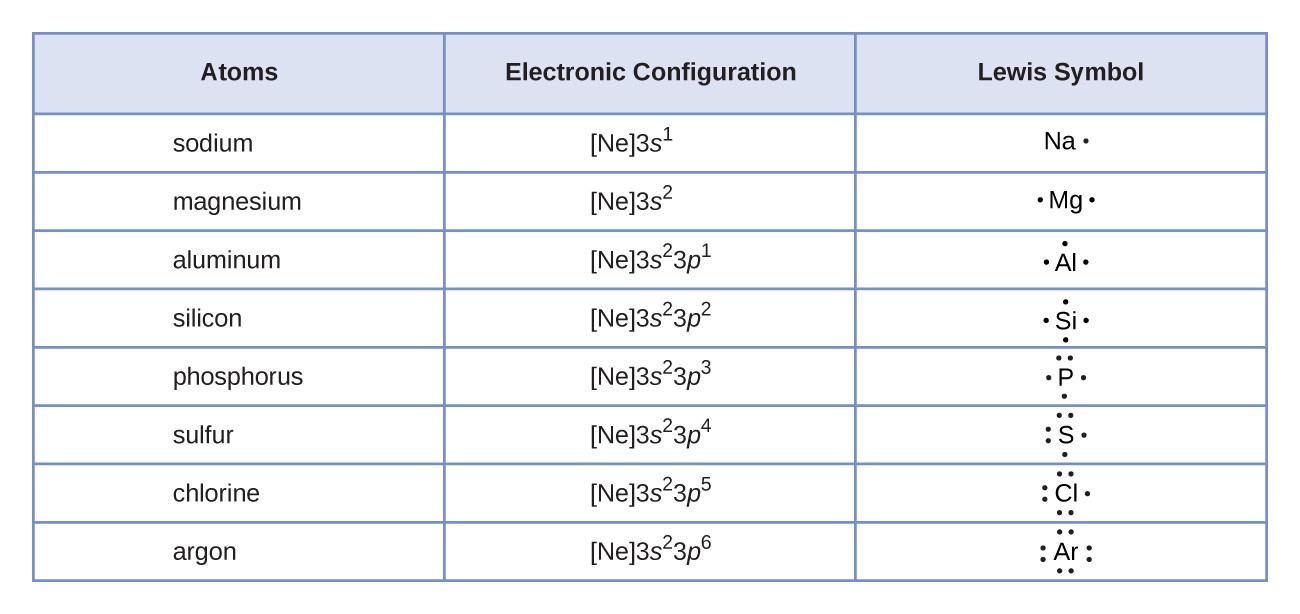
www.coursehero.com
AsF5 Lewis Structure, Geometry, And Hybridization – Chemistry Steps
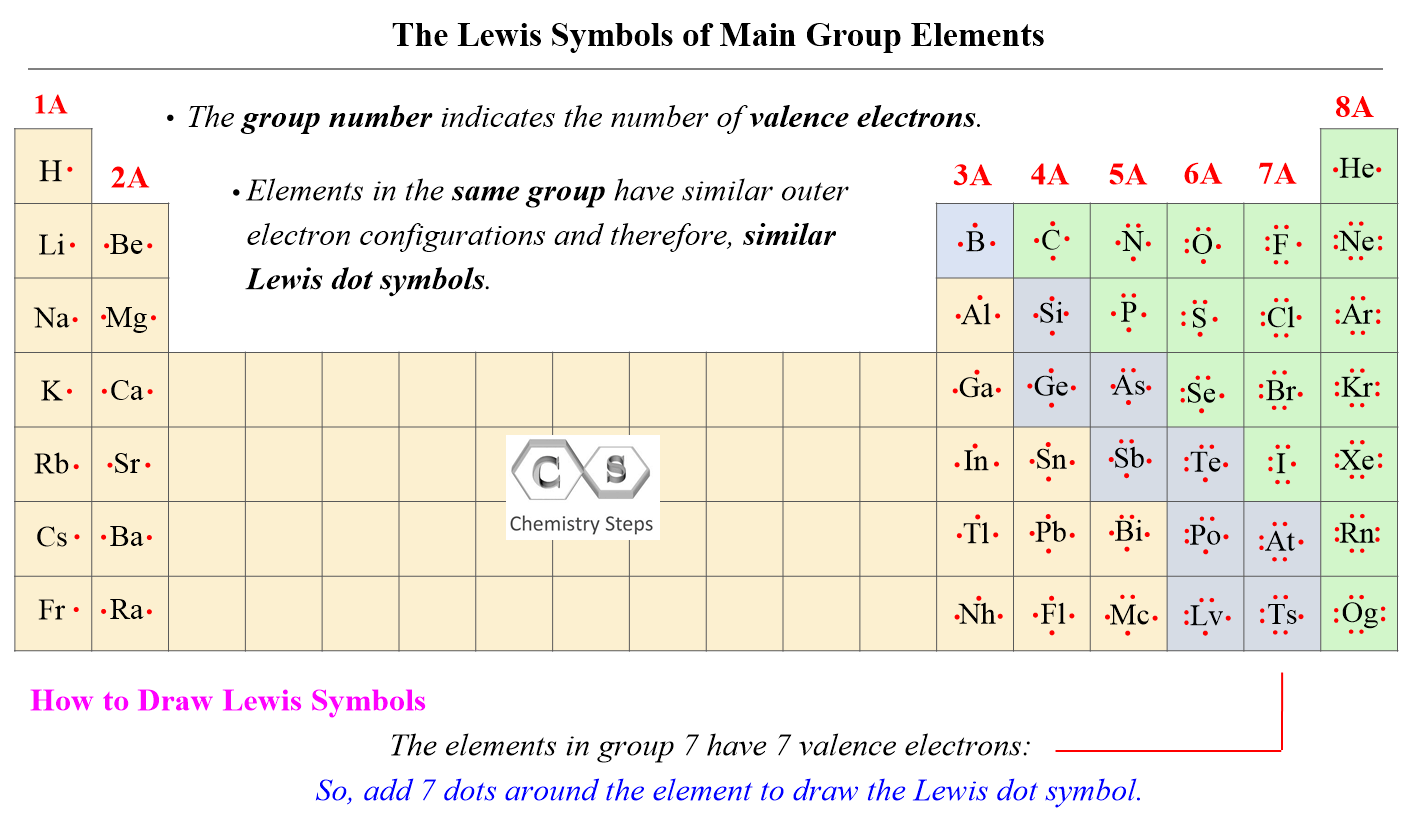
general.chemistrysteps.com
SO4 2- Lewis Structure In 5 Steps (With Images)
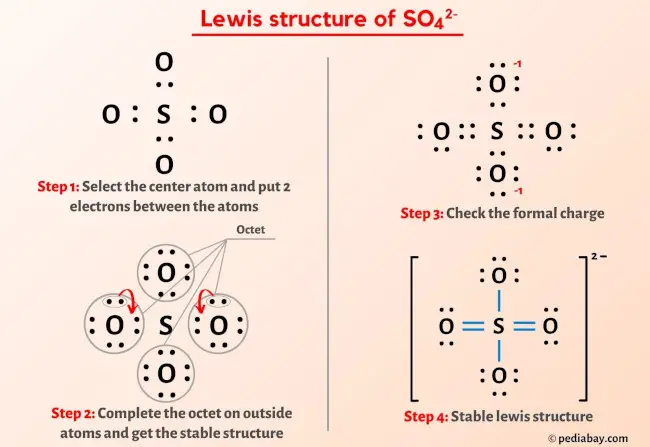
pediabay.com
Lewis Structure Of H2CO [with Video And Free Study Guide]
![Lewis Structure of H2CO [with video and free study guide]](https://www.aceorganicchem.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/H2Co-puzzle-peices.jpg)
aceorganicchem.com
BeCl2 Lewis Structure In 6 Steps (With Images)
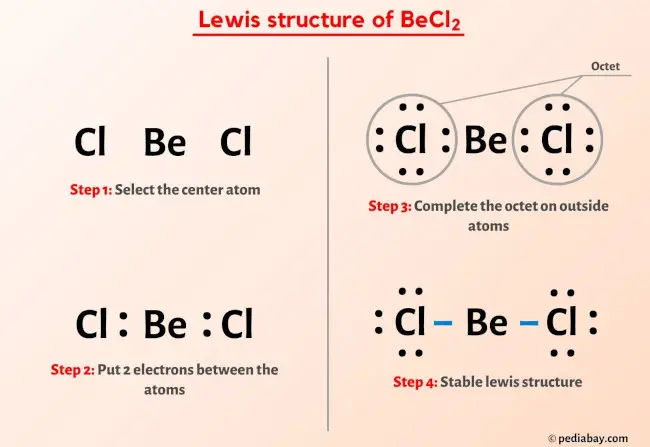
pediabay.com
F2O Lewis Structure: How To Draw The Lewis Structure For F2O

www.youtube.com
Portrait Of G. N. Lewis, Approx. 1930. – Pictures And Illustrations

scarc.library.oregonstate.edu
Hocl lewis structure: how to draw lewis dot structure. F2o lewis structure: how to draw the lewis structure for f2o …. David coulthard's theory on lewis hamilton's mercedes contract delay …