Are you diving into the fascinating world of biology and exploring the intricacies of the cell? Understanding the cell membrane is absolutely crucial, as it’s the gatekeeper, the protector, and the communicator of every single cell in your body (and every other living organism!). But let’s be honest, staring at diagrams in textbooks can sometimes feel a bit…dry. That’s where the Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet comes to the rescue!
This engaging and interactive worksheet transforms the often-intimidating task of learning about the cell membrane into a fun and memorable experience. By actively coloring the different components of the membrane, you’ll visually reinforce your understanding of their structure and function. No more rote memorization; instead, you’ll be building lasting connections between the names and roles of each part.
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, isn’t just a simple barrier. It’s a complex and dynamic structure composed of a phospholipid bilayer, proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol (in animal cells). Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining cell integrity, facilitating transport, and enabling communication with its environment. The coloring worksheet allows you to actively identify and differentiate each of these key structures.
Beyond just labeling, the act of coloring helps solidify your understanding of spatial relationships. You’ll see how the phospholipid bilayer is arranged, how integral and peripheral proteins are embedded within it, and how carbohydrates are attached to the surface. This visual understanding is critical for grasping concepts like selective permeability and the various transport mechanisms that allow cells to take in nutrients and expel waste.
So, grab your colored pencils, markers, or even your digital drawing tablet, and prepare to embark on a colorful journey into the world of the cell membrane! With a little bit of creativity and a dash of scientific curiosity, you’ll be mastering this essential biological concept in no time. After completing the worksheet, be sure to check your answers to ensure accuracy and reinforce your learning.
Understanding the Cell Membrane: A Visual Guide
The following key components of the cell membrane should be clearly identifiable on your completed coloring worksheet. Pay close attention to their location and arrangement within the membrane structure.
Key Components to Color and Identify:
- Phospholipid Bilayer: The foundation of the cell membrane, consisting of two layers of phospholipid molecules.
- Phospholipid Heads: The hydrophilic (water-loving) portion of the phospholipid, facing outwards towards the aqueous environments.
- Phospholipid Tails: The hydrophobic (water-fearing) portion of the phospholipid, facing inwards towards each other within the bilayer.
- Integral Proteins: Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, often spanning the entire membrane.
- Peripheral Proteins: Proteins associated with the surface of the phospholipid bilayer, either on the inner or outer leaflet.
- Cholesterol (in animal cells): A lipid molecule embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, providing stability and fluidity to the membrane.
- Glycolipids: Lipids with carbohydrate chains attached, found on the outer surface of the cell membrane, involved in cell recognition.
- Glycoproteins: Proteins with carbohydrate chains attached, also found on the outer surface of the cell membrane, involved in cell signaling and adhesion.
- Channel Proteins: Integral proteins that form pores or channels through the membrane, allowing specific molecules to pass through.
- Carrier Proteins: Integral proteins that bind to specific molecules and undergo a conformational change to transport them across the membrane.
Answer Key: Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet
Here is the answer key to the Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet. Use this to check your work and reinforce your understanding. Remember, accurate identification and coloring are crucial for building a solid foundation in cell biology!
- Phospholipid Bilayer: Should be represented as two distinct layers running the length of the membrane. The color should be consistent for both layers.
- Phospholipid Heads: Should be colored a consistent color, distinct from the tails, and should face outwards (towards the top and bottom of the diagram, representing the aqueous environments).
- Phospholipid Tails: Should be colored a different color than the heads, and should face inwards, towards each other, forming the hydrophobic core of the membrane.
- Integral Proteins: Should be colored a separate color and clearly shown embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, sometimes spanning the entire membrane (transmembrane proteins). Different shapes and orientations can be used to represent different types of integral proteins.
- Peripheral Proteins: Should be colored a different color from the integral proteins and shown attached to the surface of the membrane, either on the inner or outer leaflet. They should not be embedded within the bilayer.
- Cholesterol (in animal cells): Should be represented by smaller structures embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, typically interspersed among the phospholipid tails. Use a distinct color.
- Glycolipids: Should be colored a distinct color from the phospholipids, with a carbohydrate chain (often represented as a branching structure) extending outwards from the outer leaflet of the membrane.
- Glycoproteins: Should be colored a distinct color from the integral and peripheral proteins, with a carbohydrate chain (often represented as a branching structure) extending outwards from the outer leaflet of the membrane.
- Channel Proteins: These should be a specific type of integral protein forming a channel or pore through the membrane. Color distinctly, showing the opening through the membrane.
- Carrier Proteins: These should be a specific type of integral protein. Color distinctly and consider illustrating that they bind to specific molecules and undergo a shape change during transport.
If you are looking for Cell you’ve came to the right place. We have 20 Pictures about Cell like Definition of cell – NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms – NCI, Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial and also Cell. Here it is:
Cell

ar.inspiredpencil.com
Research On Cells | Create WebQuest
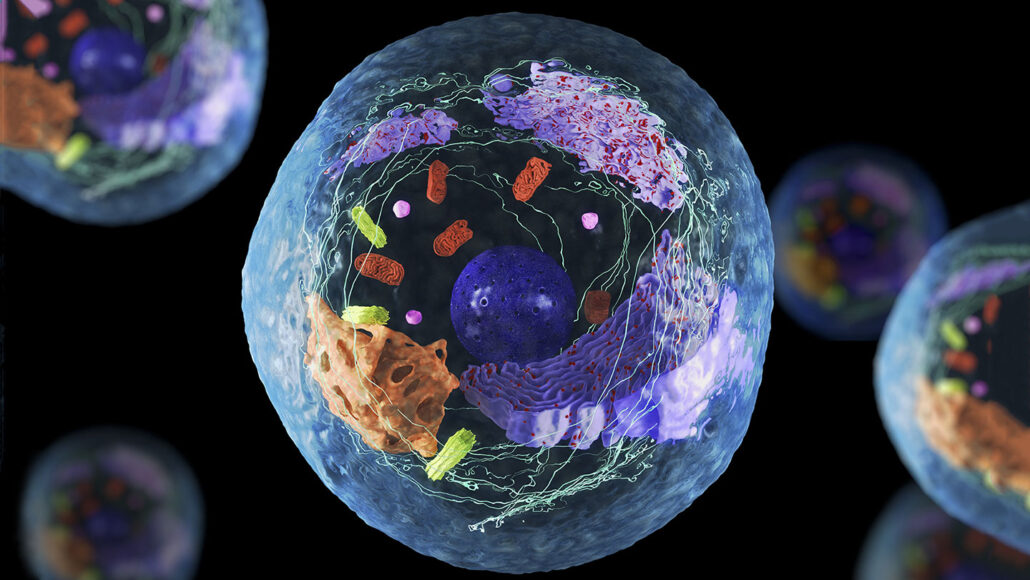
www.createwebquest.com
Animal Cell Organelles By Teach Simple

teachsimple.com
Human Cell Membrane
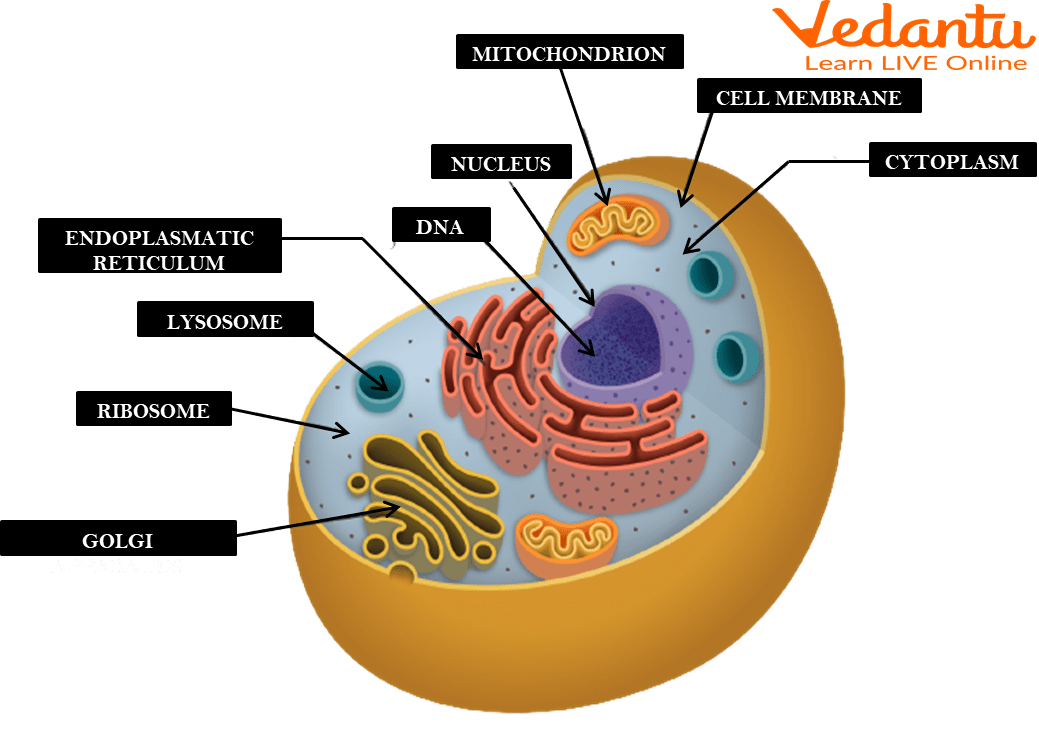
ar.inspiredpencil.com
Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial
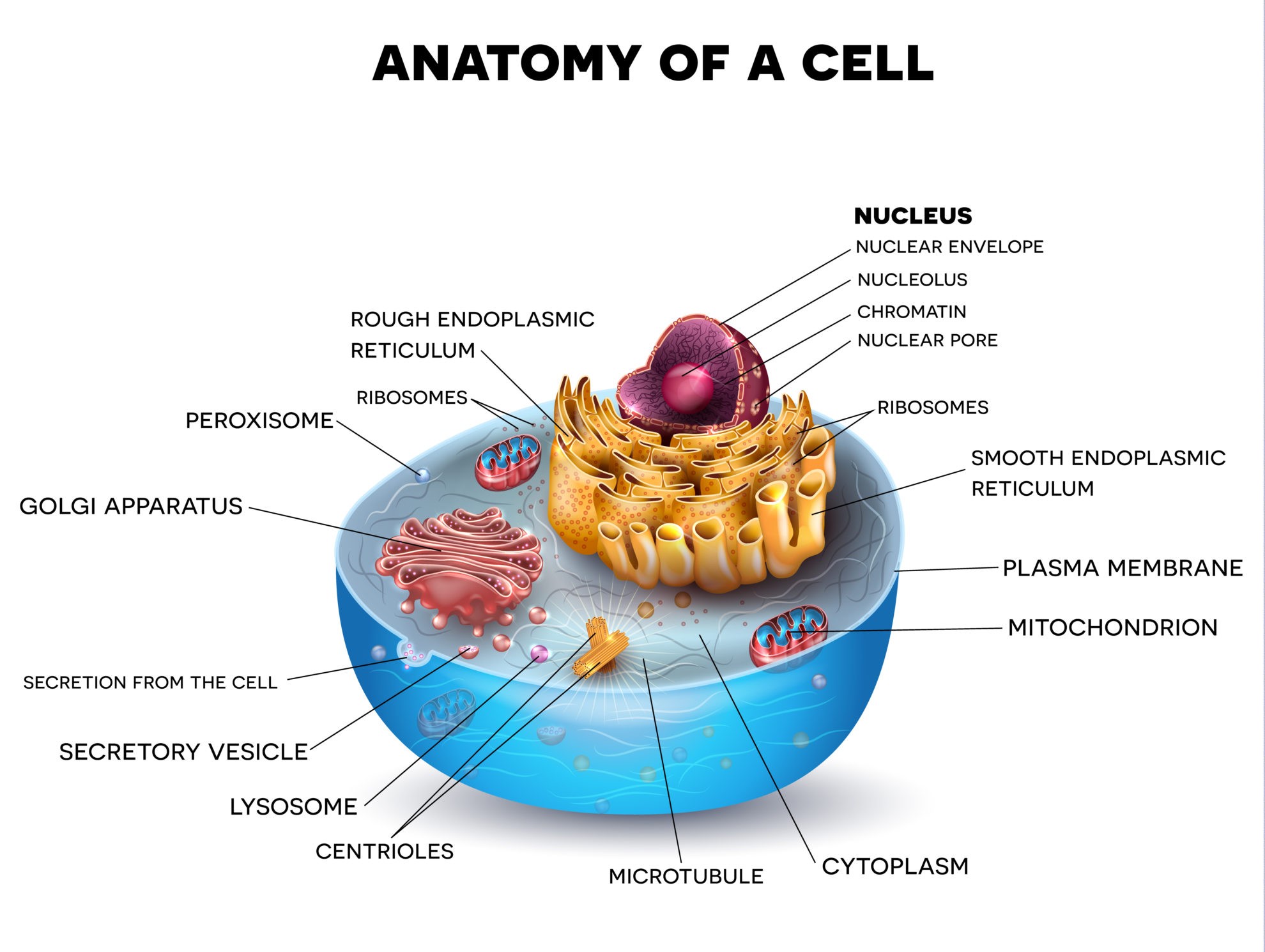
www.biologyonline.com
Issue: Trends In Cell Biology

www.cell.com
Animal Cell Model Labeled And Functions

lessonlibletterings.z22.web.core.windows.net
10 Mind-Blowing Facts About Cells You Need To Know – Sci Chores

scichores.com
Cell – Proteins, Structure, Function | Britannica

www.britannica.com
Microtubule Animal Cell
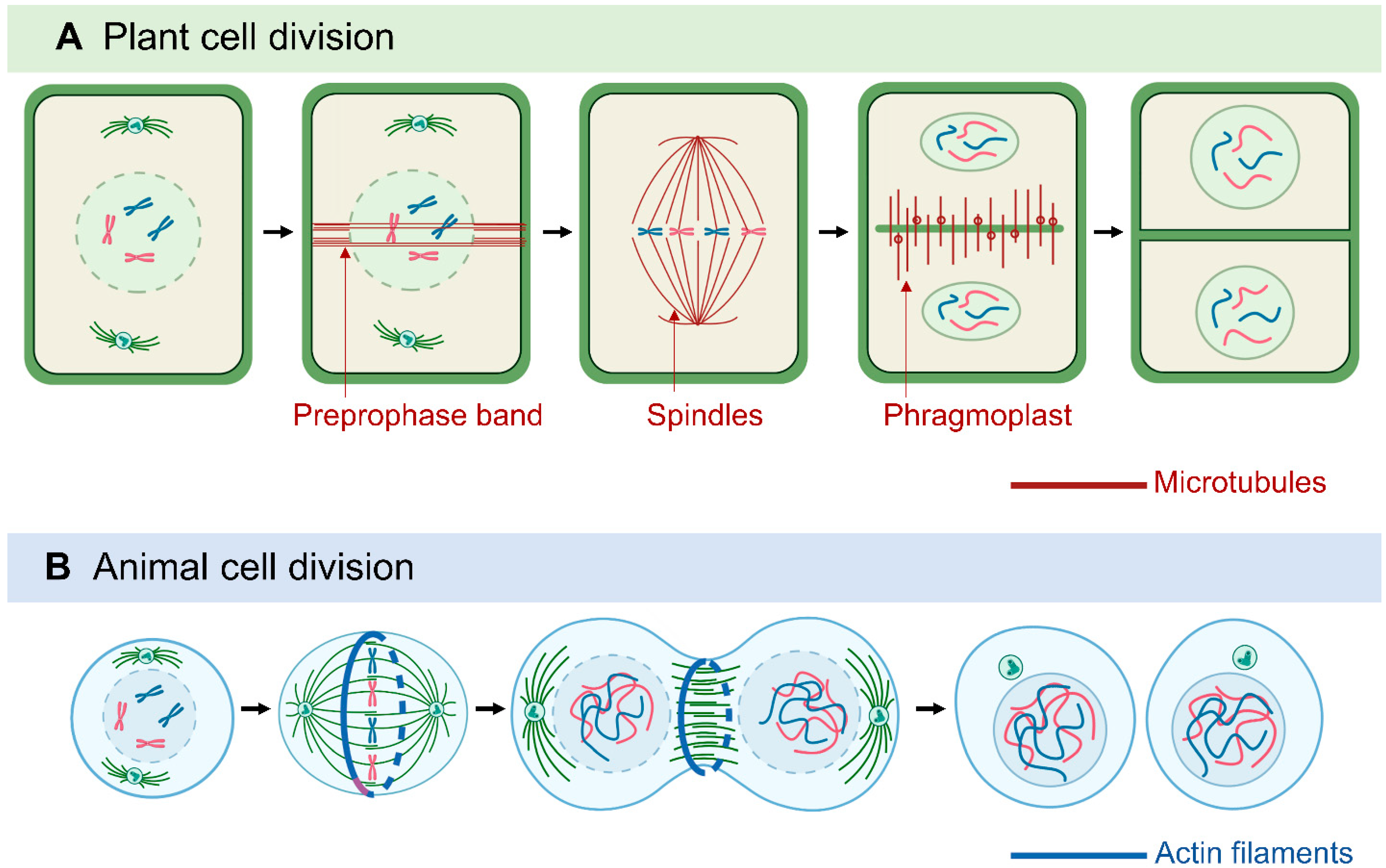
animalia-life.club
Célula Animal Célula Animal PNG ,dibujos Célula Animal, Células, Ipa

es.pngtree.com
Animal Cell – Diagram, Organelles, And Characteristics | Cell Diagram

www.pinterest.com
Animal Cell Structure
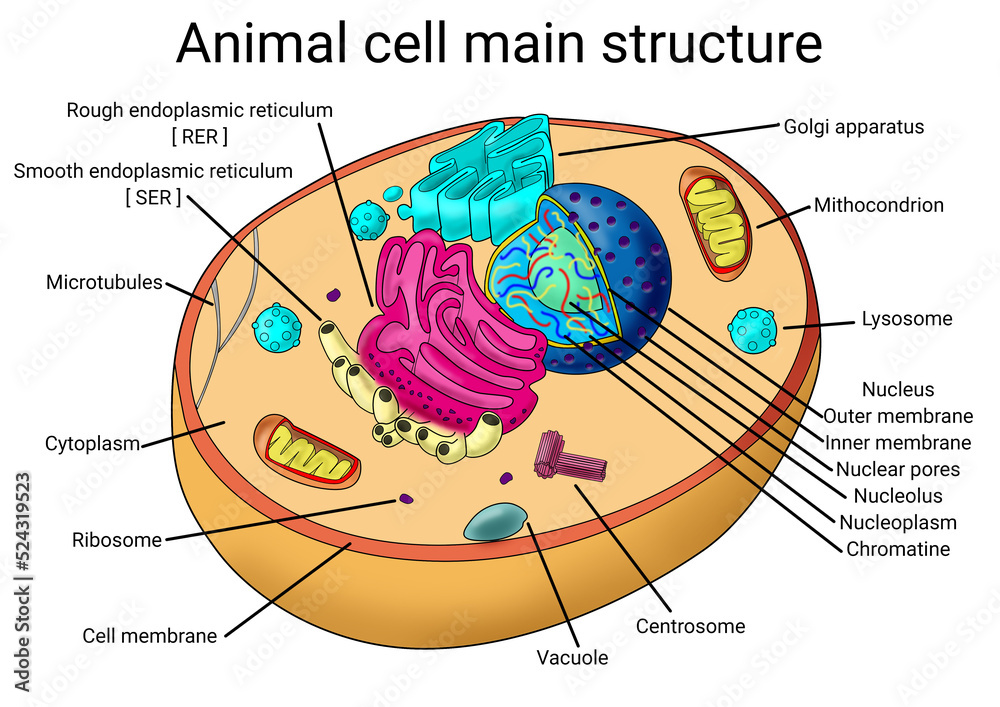
animalia-life.club
Definition Of Cell – NCI Dictionary Of Cancer Terms – NCI
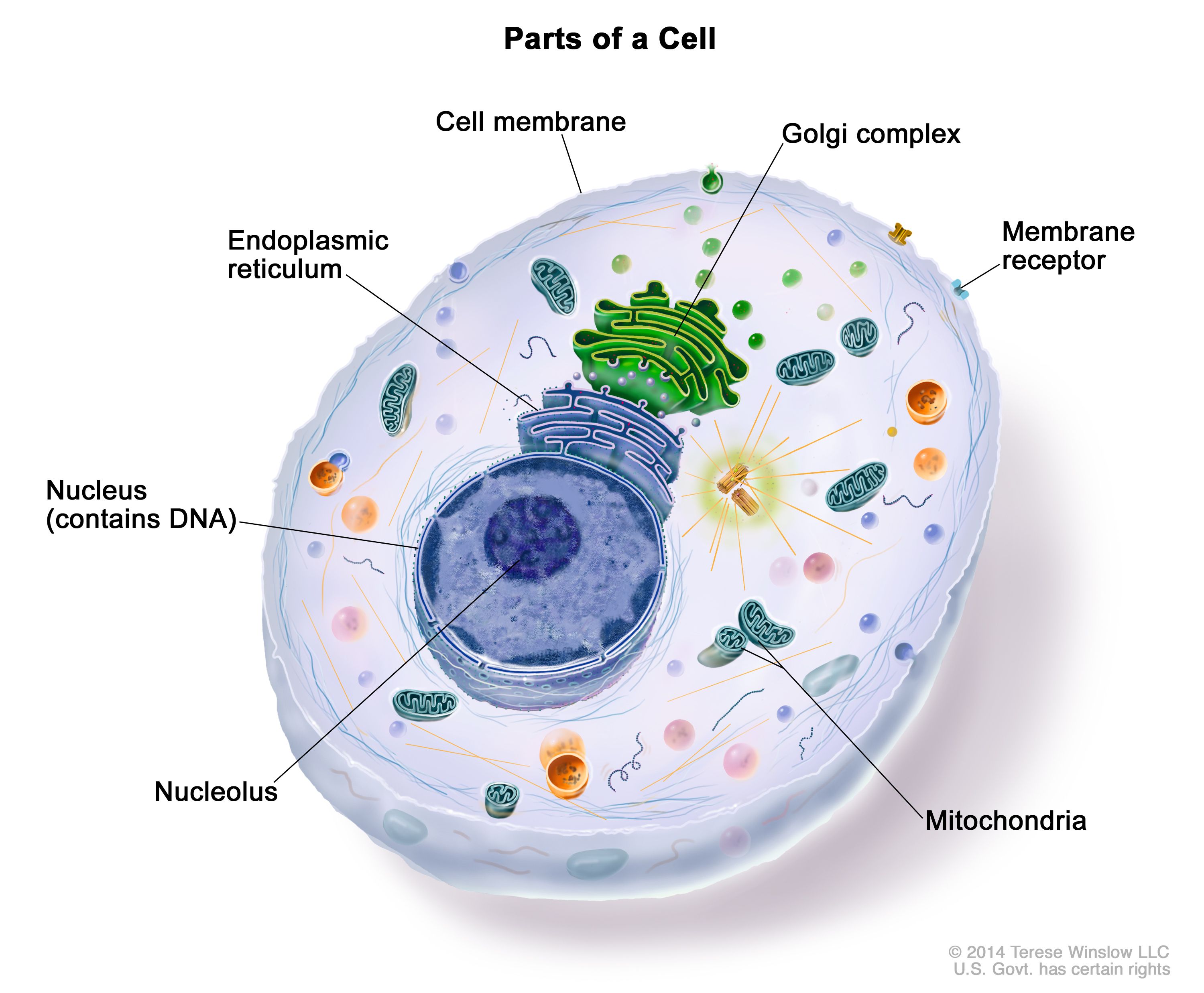
www.cancer.gov
Plant And Animal Cell Diagram Labeled

wirepartfrontwards.z14.web.core.windows.net
What Does E Mean In Math? | TEL Gurus

telgurus.co.uk
Cell Labelled Diagram Hi-res Stock Photography And Images – Alamy
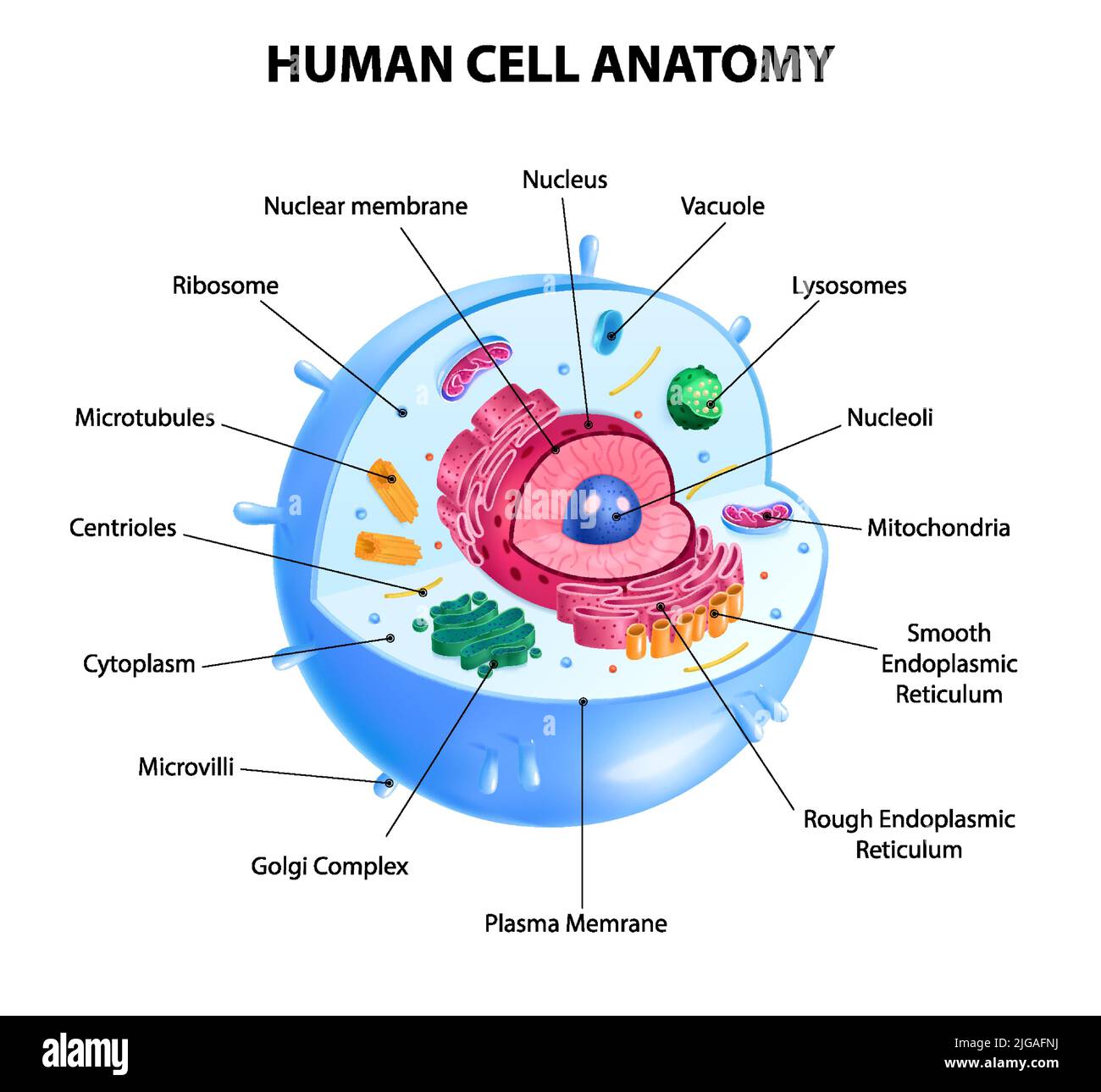
www.alamy.com
Cell Biology Flashcards | Quizlet

quizlet.com
Cell Nucleus Biology Organelles – Atiara Diguna

atiaradiguna.blogspot.com
What Is An Animal Cell? | Definition And Functions | Twinkl
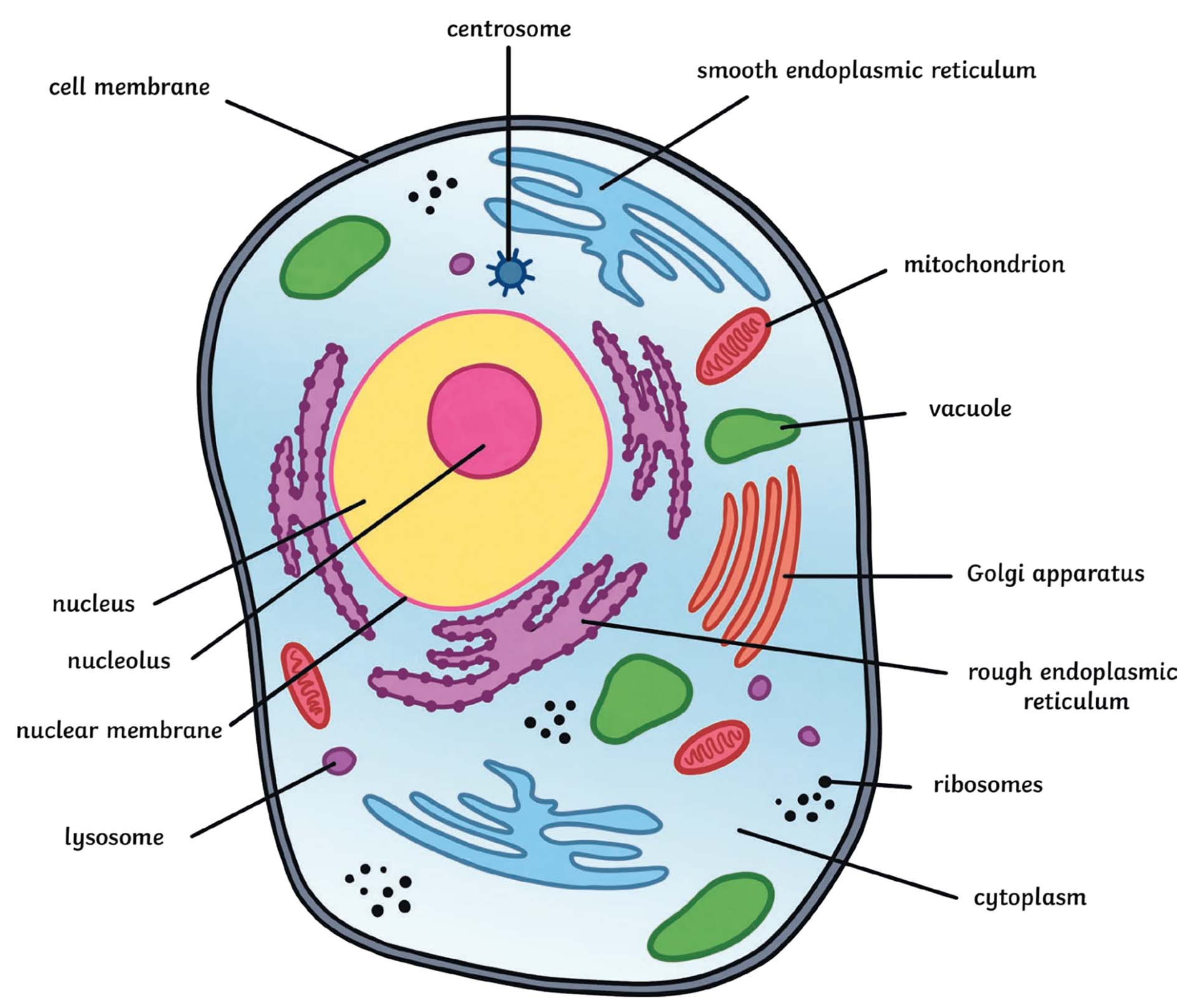
www.twinkl.pl
Animal cell model labeled and functions. What does e mean in math?. Plant and animal cell diagram labeled