Struggling to help your students master the intricate world of cell organelles? Are you tired of grading stacks of Cell Organelles Worksheets? You’ve come to the right place! Understanding the function of each organelle within a cell is crucial for building a strong foundation in biology. This post provides a comprehensive answer key to a typical Cell Organelles Worksheet, offering a valuable resource for both educators and students. Use this key to efficiently check student work, reinforce learning, and identify areas where students might need additional support.
Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
This answer key covers common cell organelles and their respective functions. Remember that the exact wording might vary slightly depending on the specific worksheet, but the underlying concepts should remain consistent. We’ll also touch upon some variations and related concepts to help broaden your understanding.
Below is the answer key, presented in a clear and organized format. This will allow for easy comparison and identification of correct answers. This resource is intended to aid in learning and teaching, not to be used for cheating. Always strive to understand the underlying concepts and functions of each organelle!
Common Cell Organelles and Their Functions
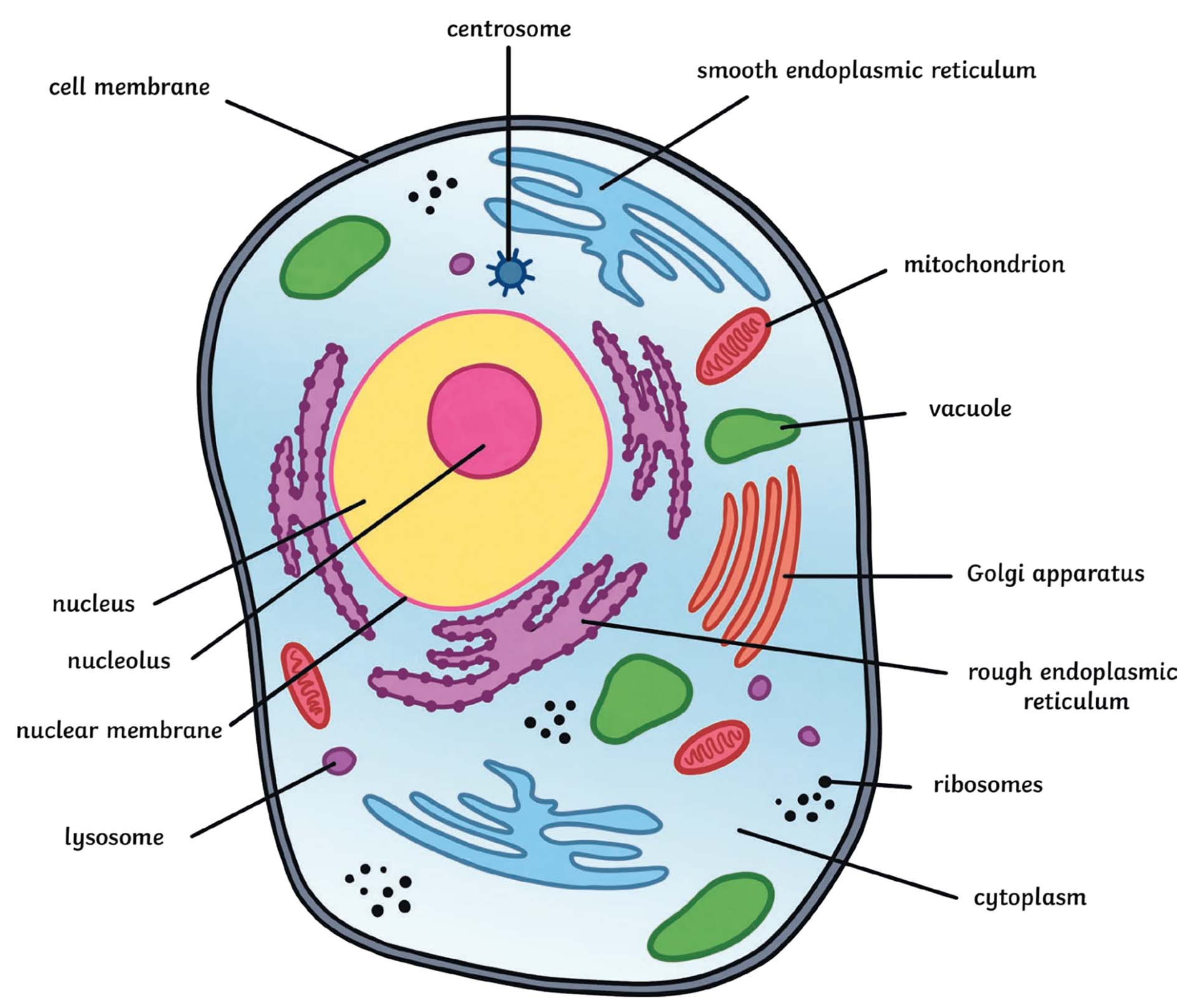
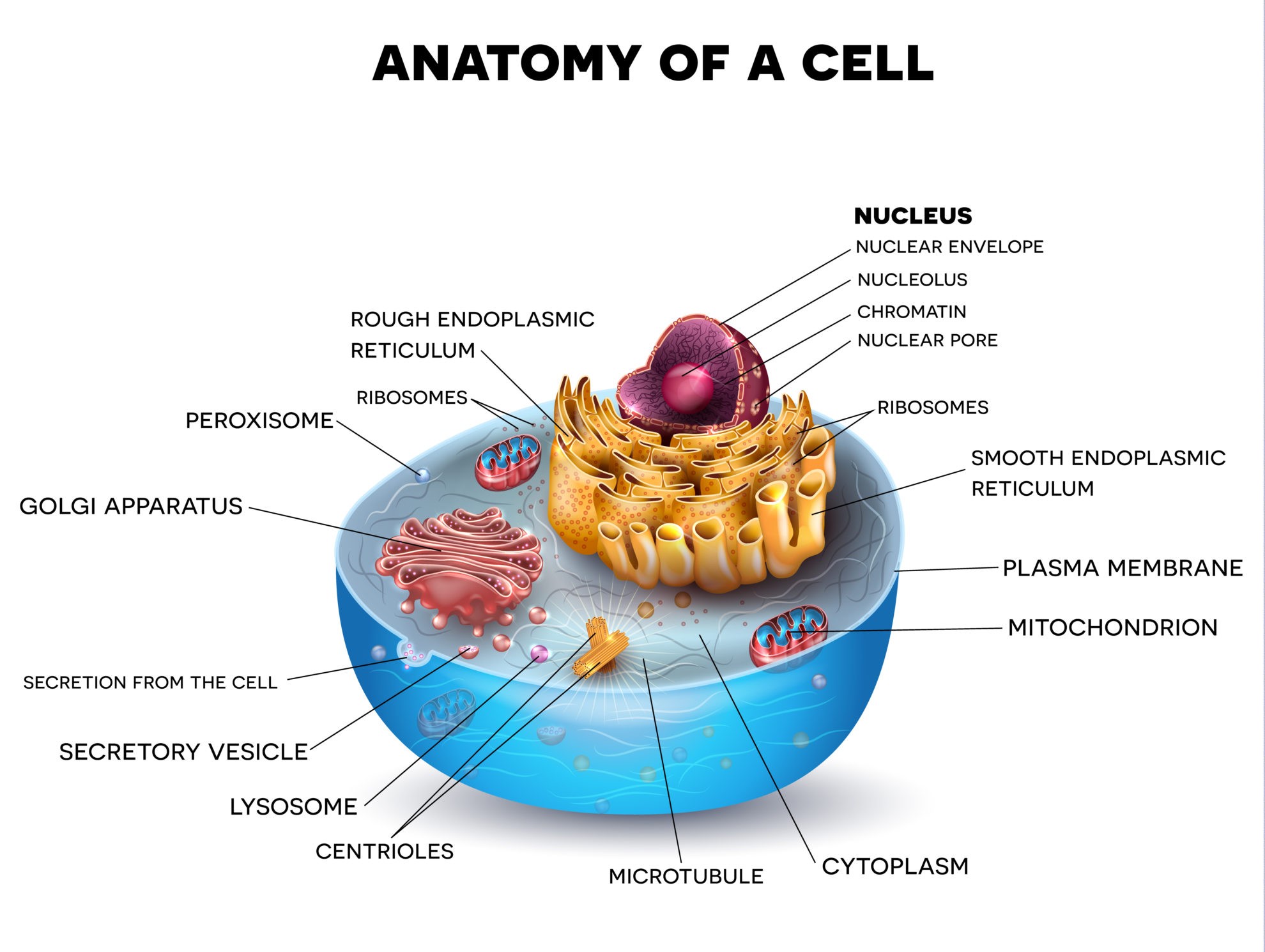
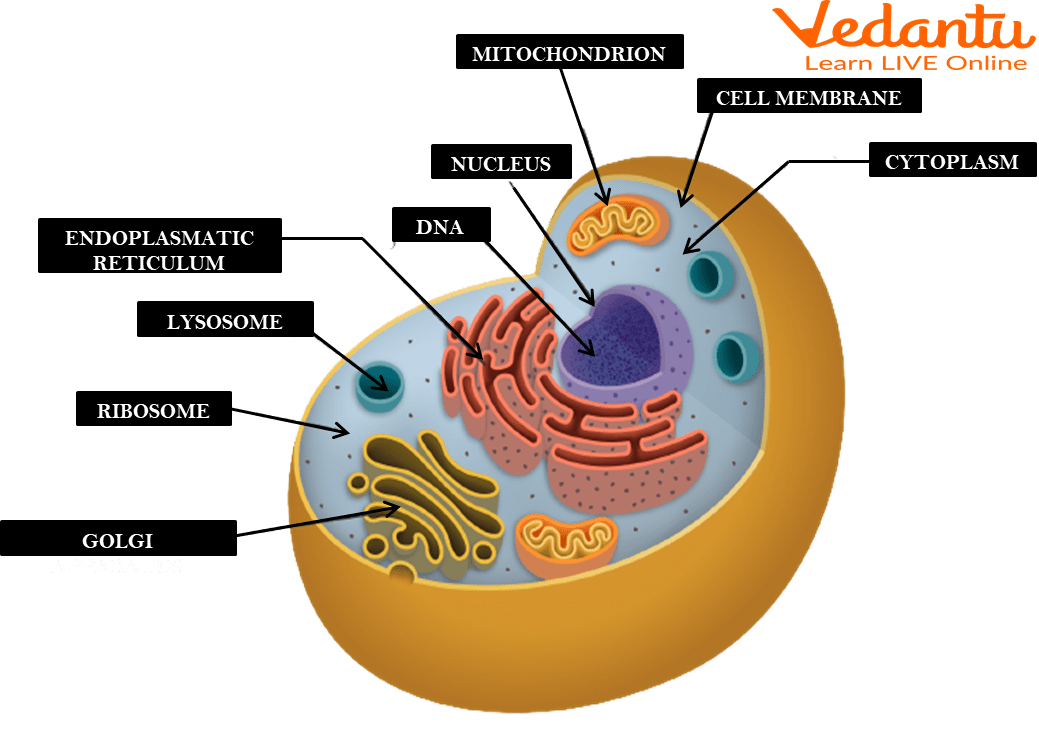
- Cell Membrane: Controls what enters and exits the cell; provides protection and support. Think of it as the gatekeeper of the cell.
- Cell Wall (Plant Cells Only): Provides rigid support and protection for the cell. It gives plants their structure.
- Cytoplasm: A gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the organelles. It’s the “soup” in which the organelles reside.
- Nucleus: Contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities. Often called the “control center” of the cell.
- Nucleolus: Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes. It’s the ribosome factory within the nucleus.
- Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins. They can be found free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis. Rough ER has ribosomes attached, while smooth ER does not.
- Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body): Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell. It’s like the cell’s packaging and shipping center.
- Lysosomes: Contain enzymes to break down waste and old cell parts. They are the cell’s “clean-up crew.”
- Vacuoles: Store water, nutrients, and waste. Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole for water storage and turgor pressure.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell; produces energy (ATP) through cellular respiration. It converts glucose into usable energy.
- Chloroplasts (Plant Cells Only): Site of photosynthesis; converts sunlight into chemical energy (glucose). This is where plants make their food.
- Cytoskeleton: A network of protein filaments that provides support and shape to the cell, and aids in movement. It’s the cell’s internal scaffolding.
- Centrioles (Animal Cells Only): Involved in cell division, forming the spindle fibers that separate chromosomes.
Variations and Related Concepts:
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Remember that prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) lack membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus. Their DNA is found in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells (like plant and animal cells) have membrane-bound organelles.
- Endosymbiotic Theory: This theory explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts. It proposes that these organelles were once free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by larger cells.
- Protein Synthesis Pathway: From DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes, ER, Golgi, and finally to their destination – understanding this pathway is key to understanding how the cell functions as a whole.
- Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Equations: Connecting the function of mitochondria and chloroplasts to the chemical equations they are involved in (cellular respiration and photosynthesis respectively) reinforces understanding.
By using this answer key effectively, you can ensure your students have a solid grasp of cell organelles and their critical roles. Remember to encourage critical thinking and deeper understanding beyond just memorizing definitions!
If you are looking for Animal Cell Model Labeled And Functions you’ve came to the right page. We have 20 Images about Animal Cell Model Labeled And Functions like Definition of cell – NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms – NCI, Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial and also Animal Cell Structure. Read more:
Animal Cell Model Labeled And Functions

lessonlibletterings.z22.web.core.windows.net
Célula Animal Célula Animal PNG ,dibujos Célula Animal, Células, Ipa

es.pngtree.com
Animal Cell Structure
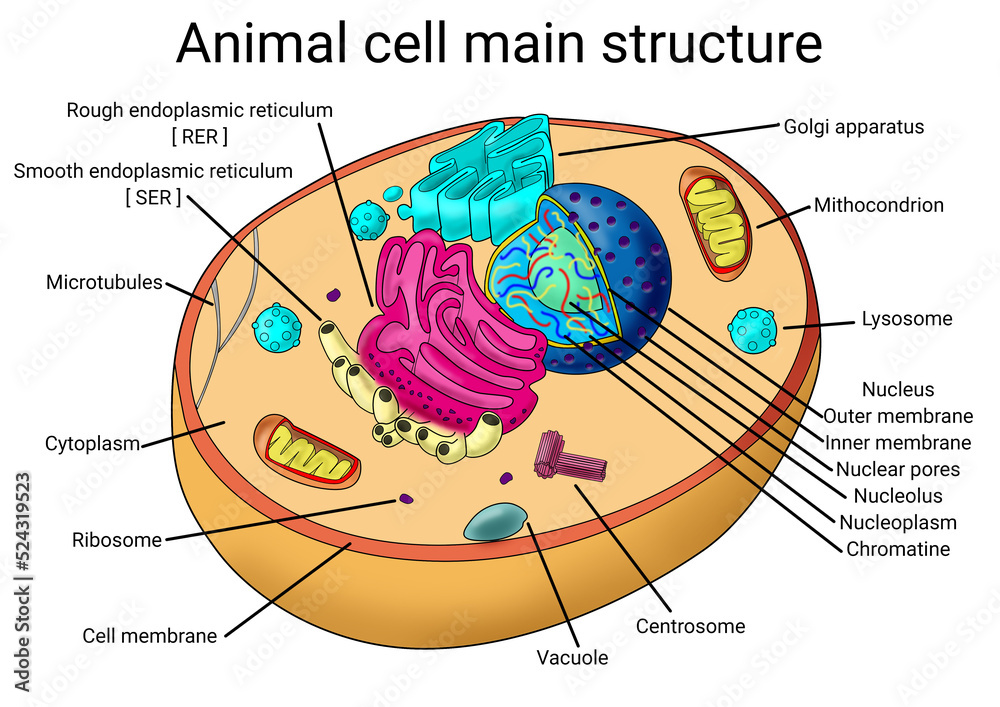
animalia-life.club
10 Mind-Blowing Facts About Cells You Need To Know – Sci Chores

scichores.com
Cell Labelled Diagram Hi-res Stock Photography And Images – Alamy
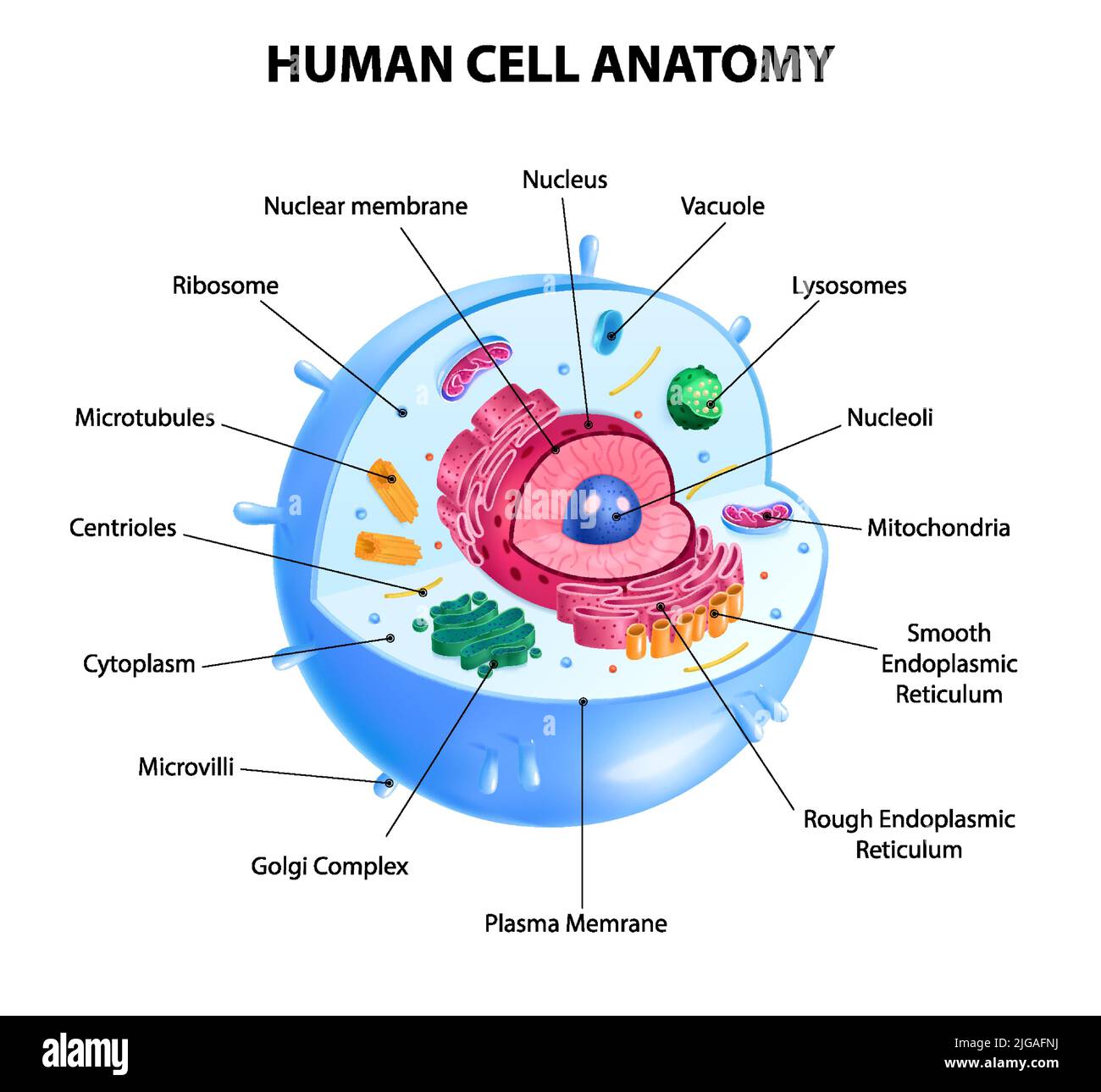
www.alamy.com
Issue: Trends In Cell Biology

www.cell.com
Cell

ar.inspiredpencil.com
Plant And Animal Cell Diagram Labeled

wirepartfrontwards.z14.web.core.windows.net
Definition Of Cell – NCI Dictionary Of Cancer Terms – NCI
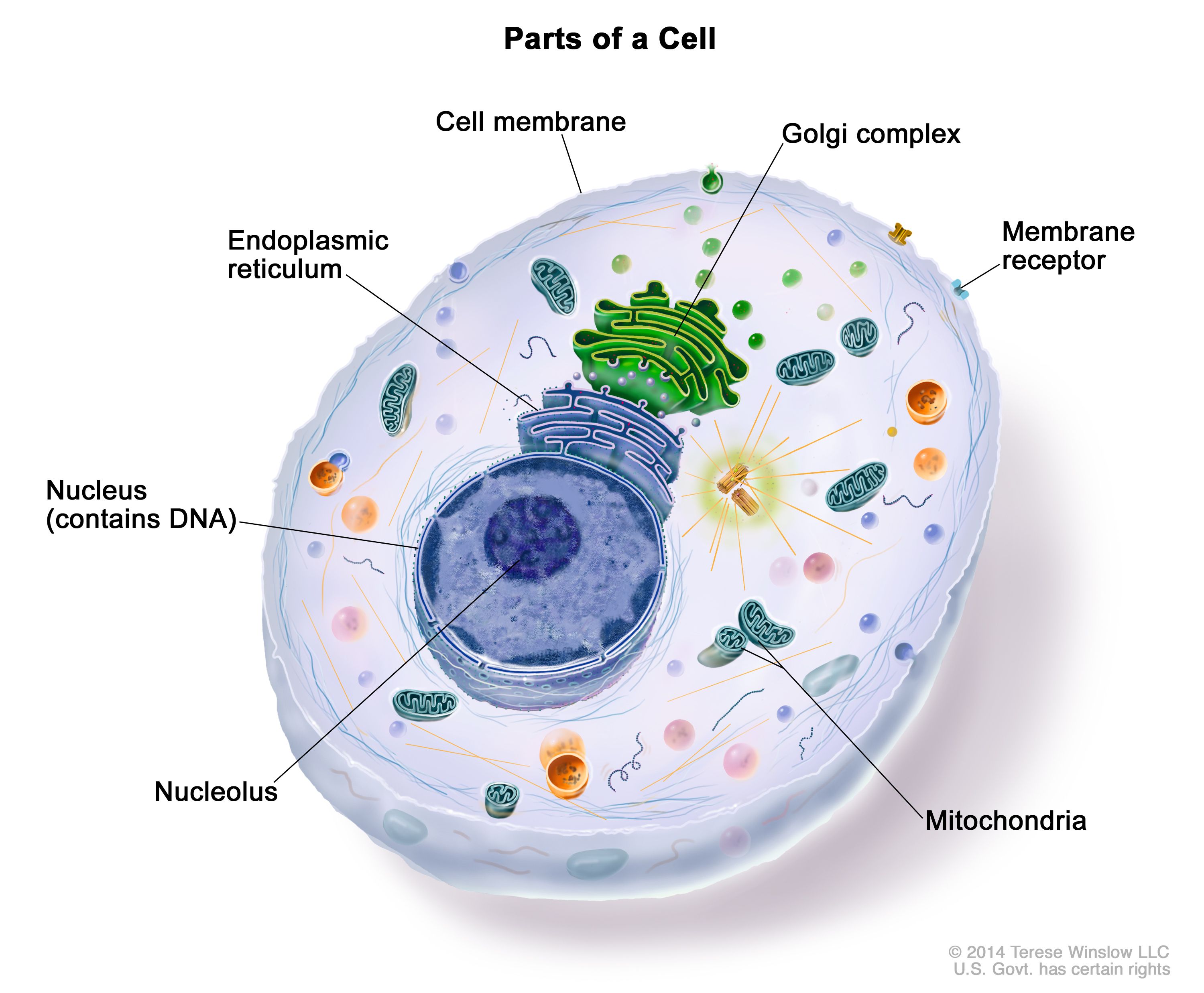
www.cancer.gov
Cell Nucleus Biology Organelles – Atiara Diguna

atiaradiguna.blogspot.com
Cell Biology Flashcards | Quizlet

quizlet.com
Microtubule Animal Cell
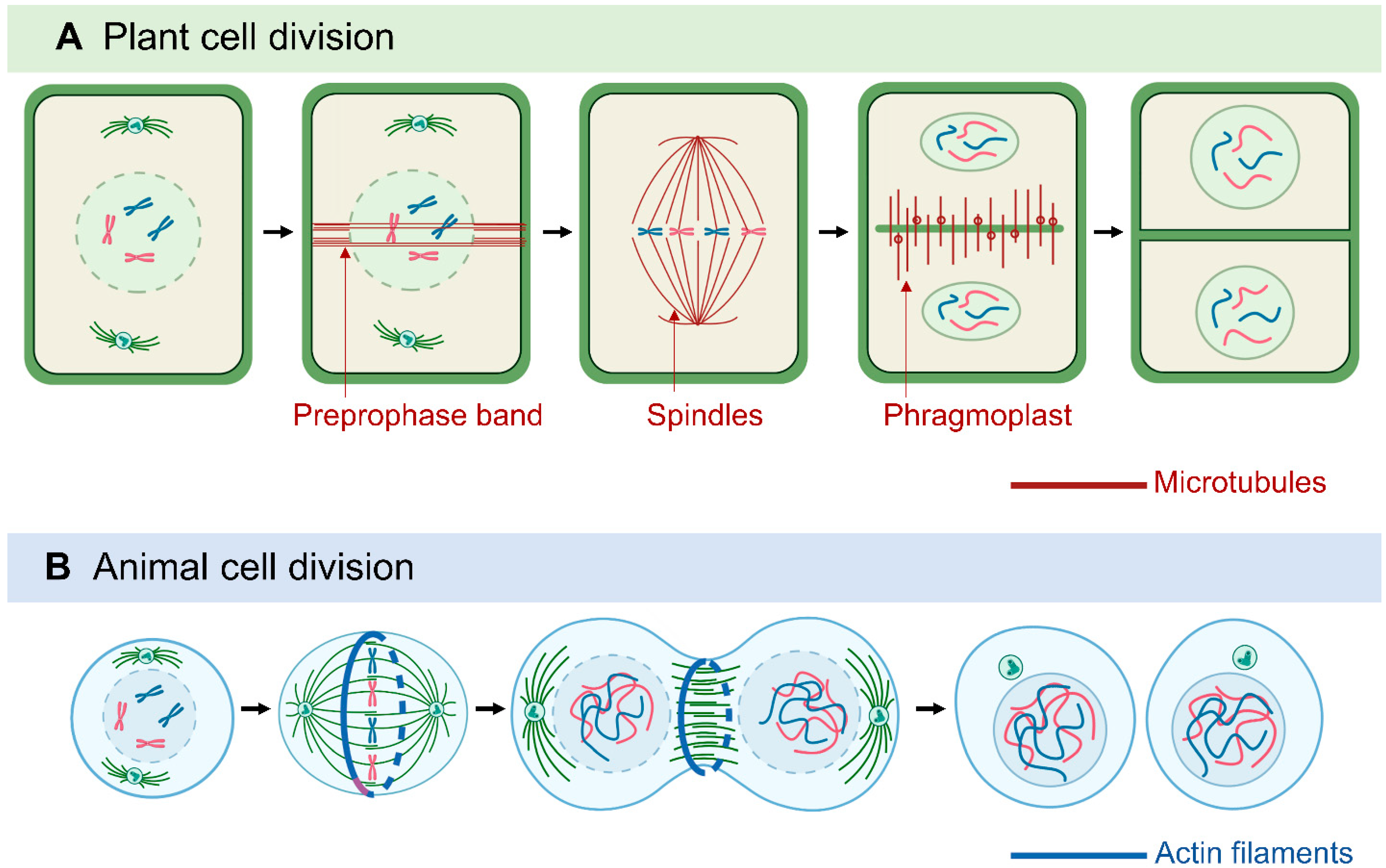
animalia-life.club
Animal Cell – Diagram, Organelles, And Characteristics | Cell Diagram

www.pinterest.com
Animal Cell Organelles By Teach Simple

teachsimple.com
Cell – Proteins, Structure, Function | Britannica

www.britannica.com
What Does E Mean In Math? | TEL Gurus

telgurus.co.uk
What Is An Animal Cell? | Definition And Functions | Twinkl
www.twinkl.pl
Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial
www.biologyonline.com
Research On Cells | Create WebQuest
www.createwebquest.com
Human Cell Membrane
ar.inspiredpencil.com
Microtubule animal cell. cell biology. Human cell membrane