Navigating the world of biology can be a fascinating journey, especially when delving into the intricacies of cell reproduction. From understanding the basic processes of mitosis and meiosis to identifying the different phases and their functions, it’s a topic that forms the foundation of many biological concepts. If you’re a student tackling a cell reproduction worksheet, you know the feeling – the pressure to recall specific terms, identify structures under a microscope (or in a diagram), and accurately describe the sequence of events. This post aims to provide you with the answers you’re likely looking for, presented in a clear and accessible format, along with some supplementary explanations to solidify your understanding.
Remember, simply memorizing answers isn’t the goal. The real value lies in comprehending the *why* behind each answer. Understanding the “why” enables you to apply the knowledge to new, unfamiliar scenarios and, more importantly, to appreciate the incredible complexity and beauty of cellular processes. Consider these answers as a guide, a launching pad for deeper exploration and critical thinking.
Below, you’ll find common questions and answers encountered in cell reproduction worksheets, presented in a concise and easy-to-understand manner. These answers are designed to help you check your work, identify areas where you may need further study, and reinforce your knowledge of the subject. Good luck with your studies!
Cell Reproduction Worksheet Answers
Mitosis and Meiosis
- Question: What is the main purpose of mitosis?
Answer: The main purpose of mitosis is cell division for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. It produces two genetically identical daughter cells. - Question: What is the main purpose of meiosis?
Answer: The main purpose of meiosis is sexual reproduction. It produces four genetically different daughter cells (gametes) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. - Question: How many cell divisions occur in mitosis?
Answer: One cell division. - Question: How many cell divisions occur in meiosis?
Answer: Two cell divisions (Meiosis I and Meiosis II). - Question: Are the daughter cells produced by mitosis identical or different to the parent cell?
Answer: Identical. - Question: Are the daughter cells produced by meiosis identical or different to the parent cell?
Answer: Different. - Question: What type of cells does mitosis occur in?
Answer: Somatic cells (body cells). - Question: What type of cells does meiosis occur in?
Answer: Germ cells (cells that produce gametes). - Question: What is crossing over, and in which process does it occur?
Answer: Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It occurs during Prophase I of meiosis. This exchange leads to genetic variation in the daughter cells. - Question: What is independent assortment, and in which process does it occur?
Answer: Independent assortment is the random alignment and separation of homologous chromosomes during Metaphase I of meiosis. This randomness contributes to genetic diversity.
The Cell Cycle and its Phases
- Question: What are the major phases of the cell cycle?
Answer: The major phases of the cell cycle are Interphase (G1, S, G2) and the Mitotic (M) phase. - Question: What happens during Interphase?
Answer: Interphase is the period of cell growth and preparation for cell division. It consists of three sub-phases: G1 (growth and normal cell functions), S (DNA replication), and G2 (further growth and preparation for mitosis). - Question: What are the phases of mitosis in order?
Answer: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase (often remembered with the acronym PMAT). - Question: Describe what happens during Prophase.
Answer: The chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. - Question: Describe what happens during Metaphase.
Answer: The chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (the equator of the cell), attached to spindle fibers. - Question: Describe what happens during Anaphase.
Answer: The sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. - Question: Describe what happens during Telophase.
Answer: The chromosomes arrive at the poles, the nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes decondense. - Question: What is cytokinesis, and when does it occur?
Answer: Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two separate daughter cells. It typically occurs concurrently with Telophase. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms. In plant cells, a cell plate forms. - Question: What is the G0 phase?
Answer: The G0 phase is a resting phase of the cell cycle where the cell has exited the cycle and is not actively dividing. Some cells, like nerve cells, remain in G0 permanently.
Key Structures
- Question: What is the role of the spindle fibers?
Answer: Spindle fibers are microtubules that attach to the chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis and help to separate the sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes. - Question: What is the centromere?
Answer: The centromere is the region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids are joined. It is also the point where spindle fibers attach during cell division. - Question: What are sister chromatids?
Answer: Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a chromosome that are connected at the centromere after DNA replication. - Question: What are homologous chromosomes?
Answer: Homologous chromosomes are chromosome pairs (one from each parent) that are similar in length, gene position, and centromere location. They carry genes for the same traits.
This list covers many of the fundamental concepts you’ll encounter in a cell reproduction worksheet. Remember to actively engage with the material, using diagrams, models, and additional resources to deepen your understanding. Good luck!
If you are looking for Cell you’ve visit to the right web. We have 20 Images about Cell like Definition of cell – NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms – NCI, Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial and also Cell labelled diagram hi-res stock photography and images – Alamy. Read more:
Cell

ar.inspiredpencil.com
Animal Cell – Diagram, Organelles, And Characteristics | Cell Diagram

www.pinterest.com
Cell Biology Flashcards | Quizlet

quizlet.com
10 Mind-Blowing Facts About Cells You Need To Know – Sci Chores

scichores.com
Cell – Proteins, Structure, Function | Britannica

www.britannica.com
Animal Cell Model Labeled And Functions

lessonlibletterings.z22.web.core.windows.net
Célula Animal Célula Animal PNG ,dibujos Célula Animal, Células, Ipa

es.pngtree.com
Research On Cells | Create WebQuest
www.createwebquest.com
Animal Cell Organelles By Teach Simple

teachsimple.com
Plant And Animal Cell Diagram Labeled

wirepartfrontwards.z14.web.core.windows.net
Cell Labelled Diagram Hi-res Stock Photography And Images – Alamy
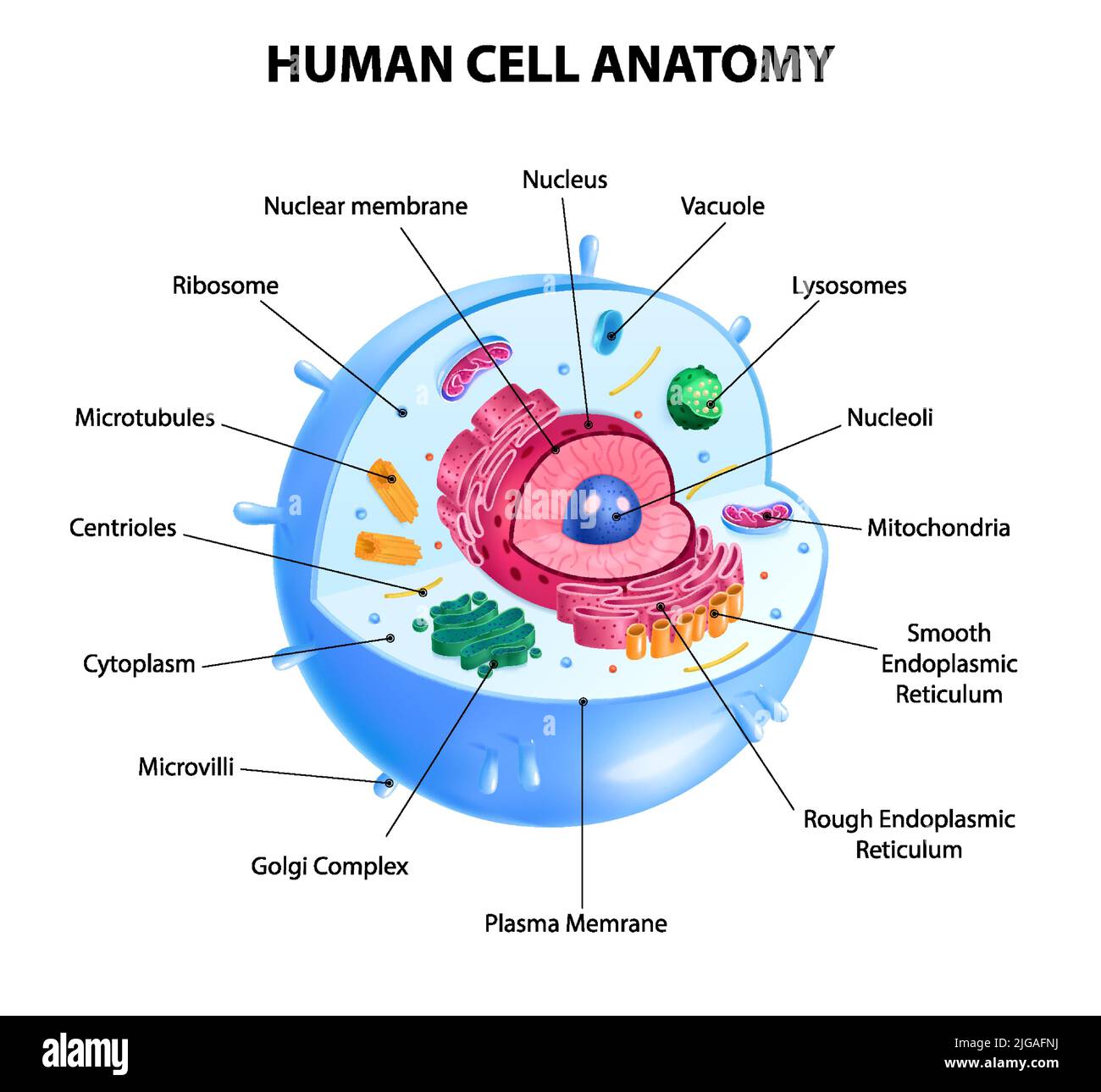
www.alamy.com
Microtubule Animal Cell
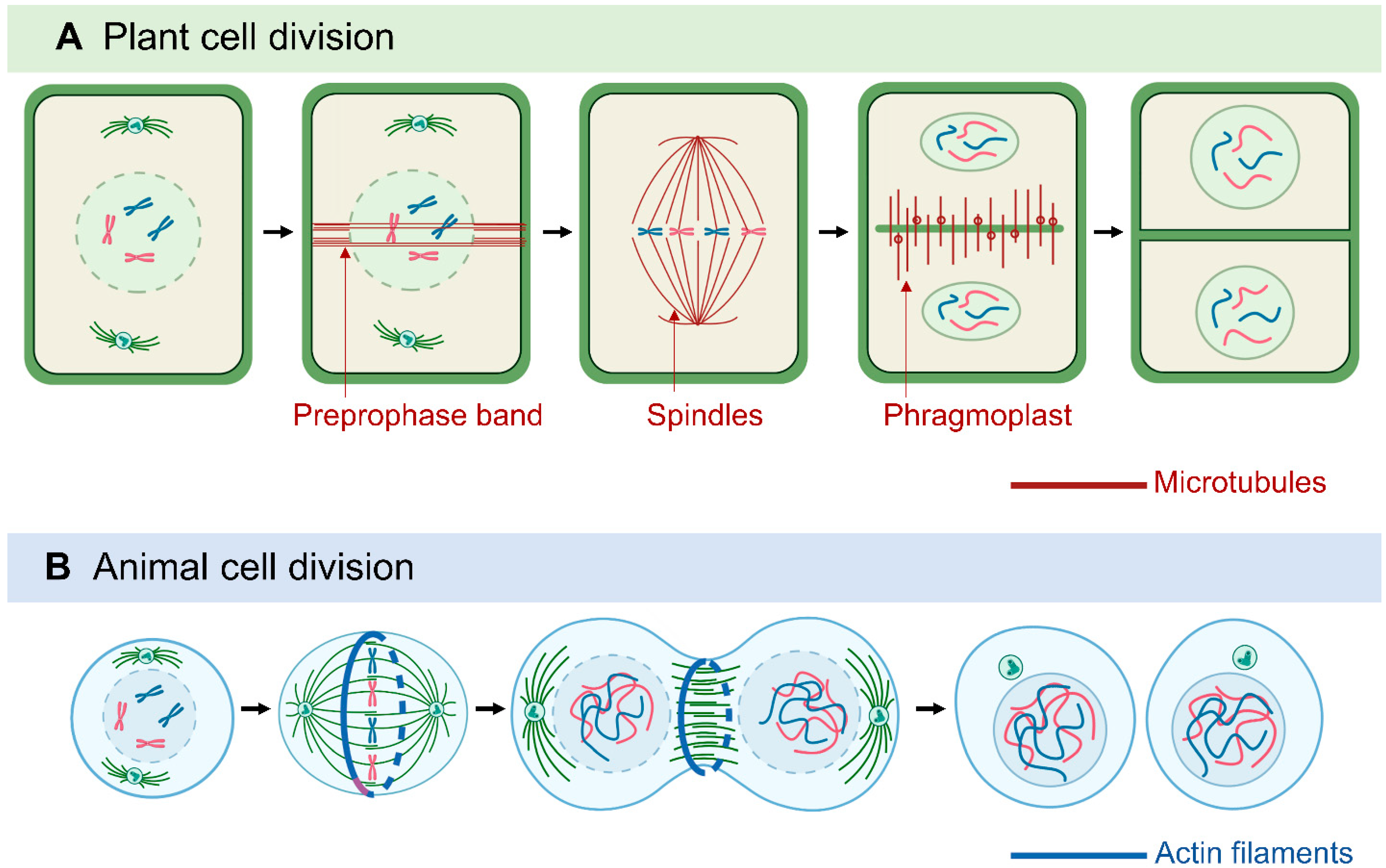
animalia-life.club
Cell Nucleus Biology Organelles – Atiara Diguna

atiaradiguna.blogspot.com
Definition Of Cell – NCI Dictionary Of Cancer Terms – NCI
www.cancer.gov
Animal Cell Structure
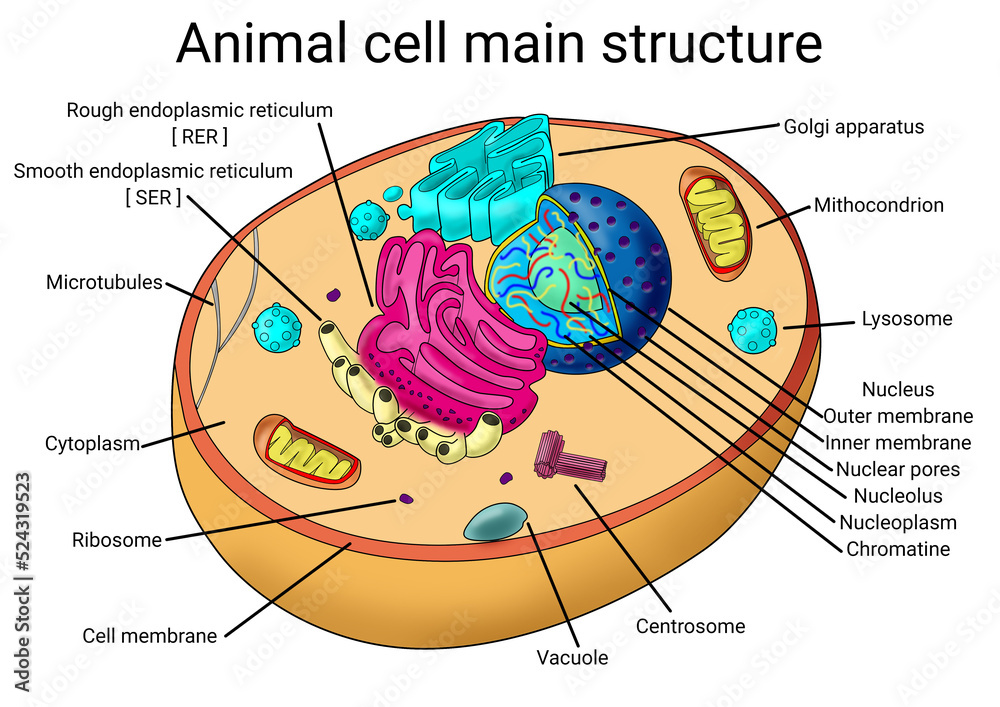
animalia-life.club
What Does E Mean In Math? | TEL Gurus

telgurus.co.uk
Cell Biology – Biology Online Tutorial
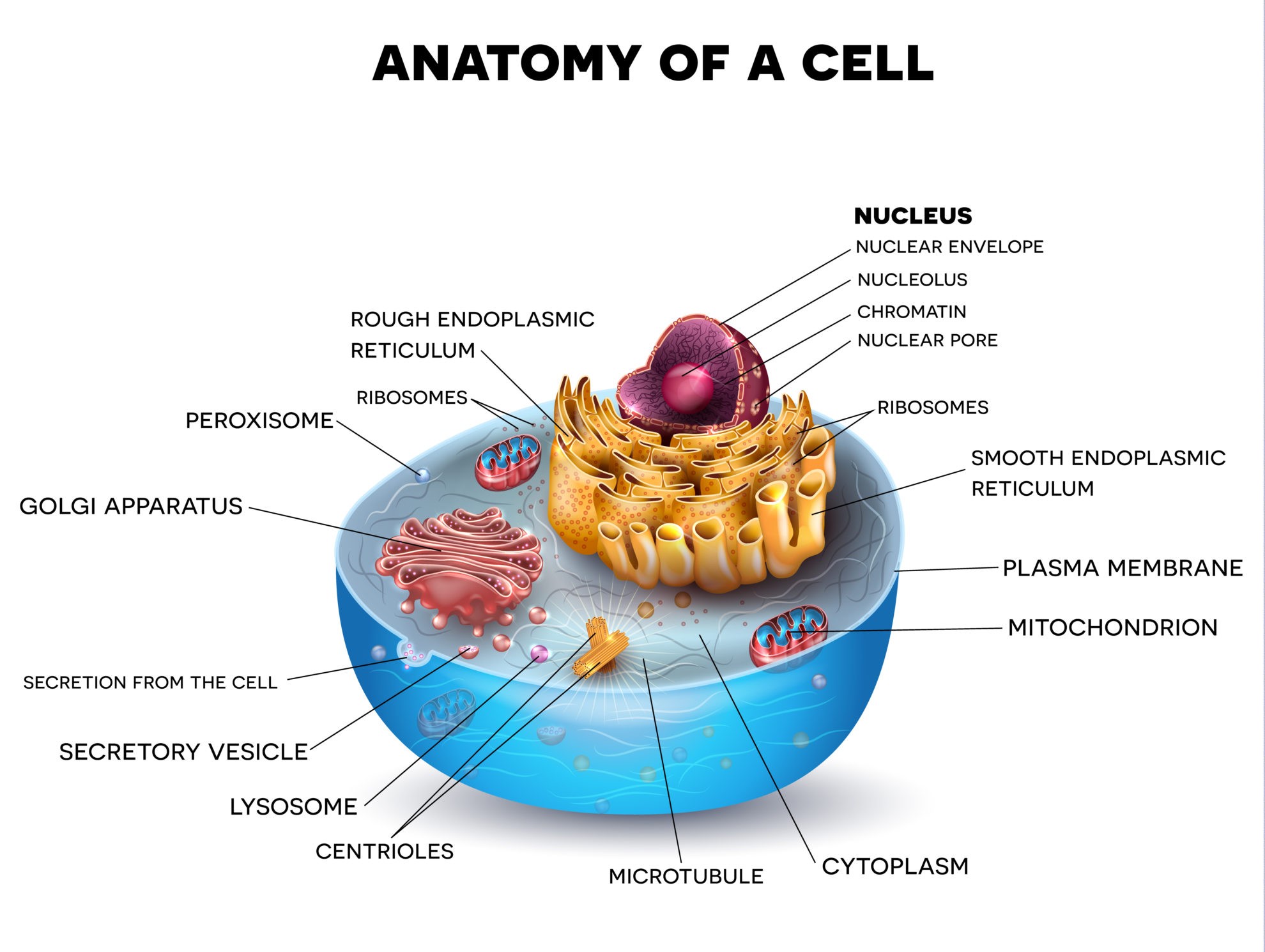
www.biologyonline.com
Issue: Trends In Cell Biology

www.cell.com
What Is An Animal Cell? | Definition And Functions | Twinkl
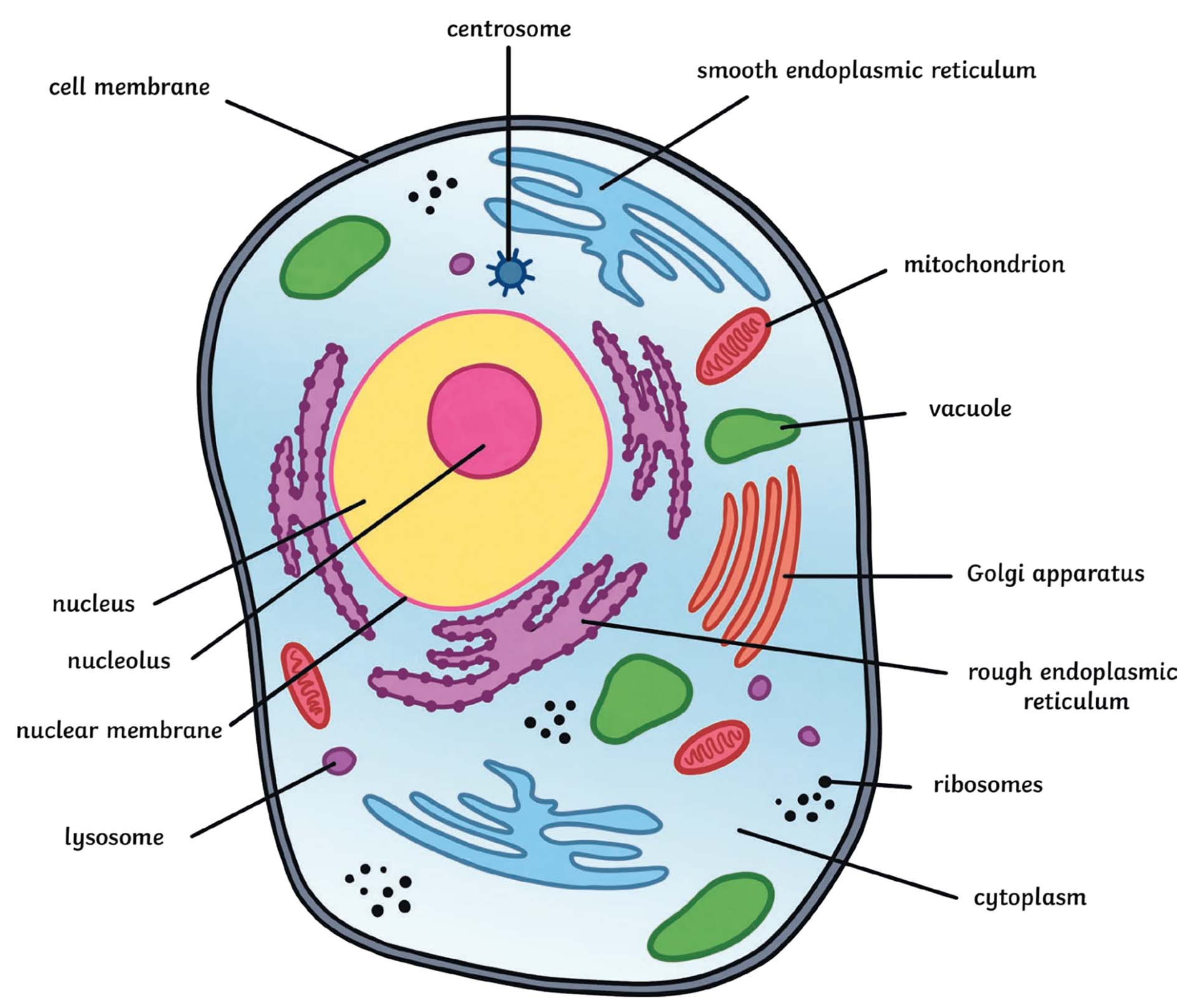
www.twinkl.pl
Human Cell Membrane
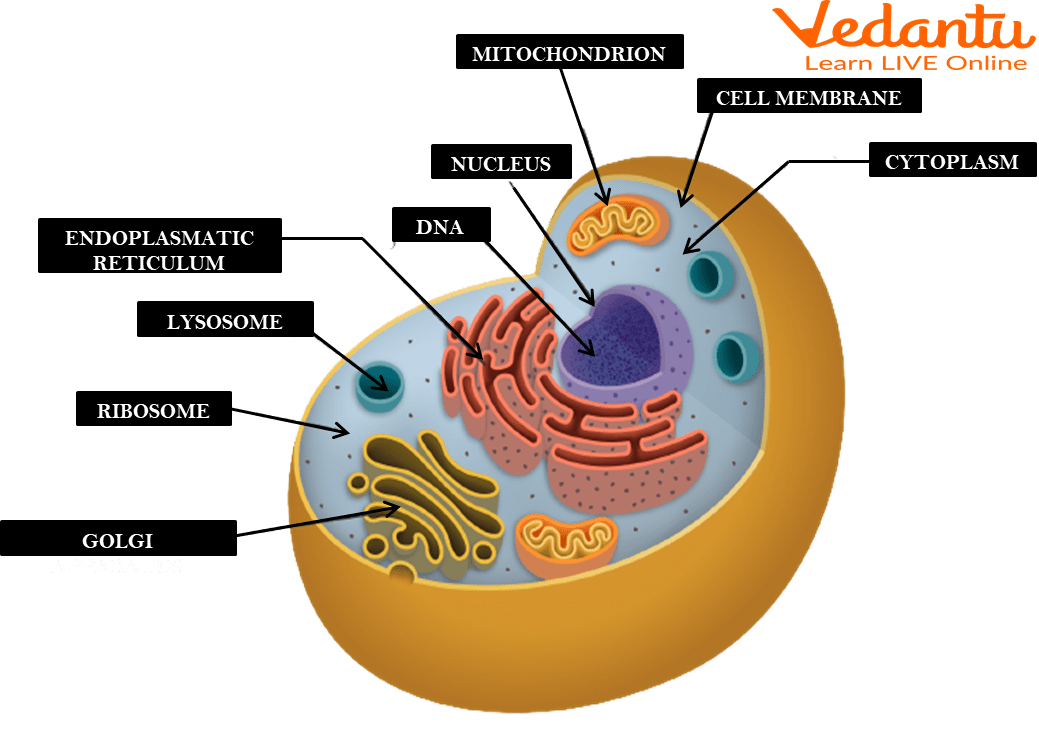
ar.inspiredpencil.com
cell biology. Animal cell. cell labelled diagram hi-res stock photography and images