Navigating the world of biology can be a fascinating journey, especially when delving into the intricate mechanisms that keep cells alive and functioning. One fundamental aspect of cellular biology is cellular transport – the process by which substances move across the cell membrane. Understanding how these processes work is crucial for grasping how cells obtain nutrients, eliminate waste, and maintain homeostasis. Worksheets are often used to reinforce learning in this area, and sometimes, checking your answers can be a sticking point. This post provides a comprehensive guide to checking your Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers, ensuring you fully understand the concepts involved.
Understanding the Basics of Cellular Transport
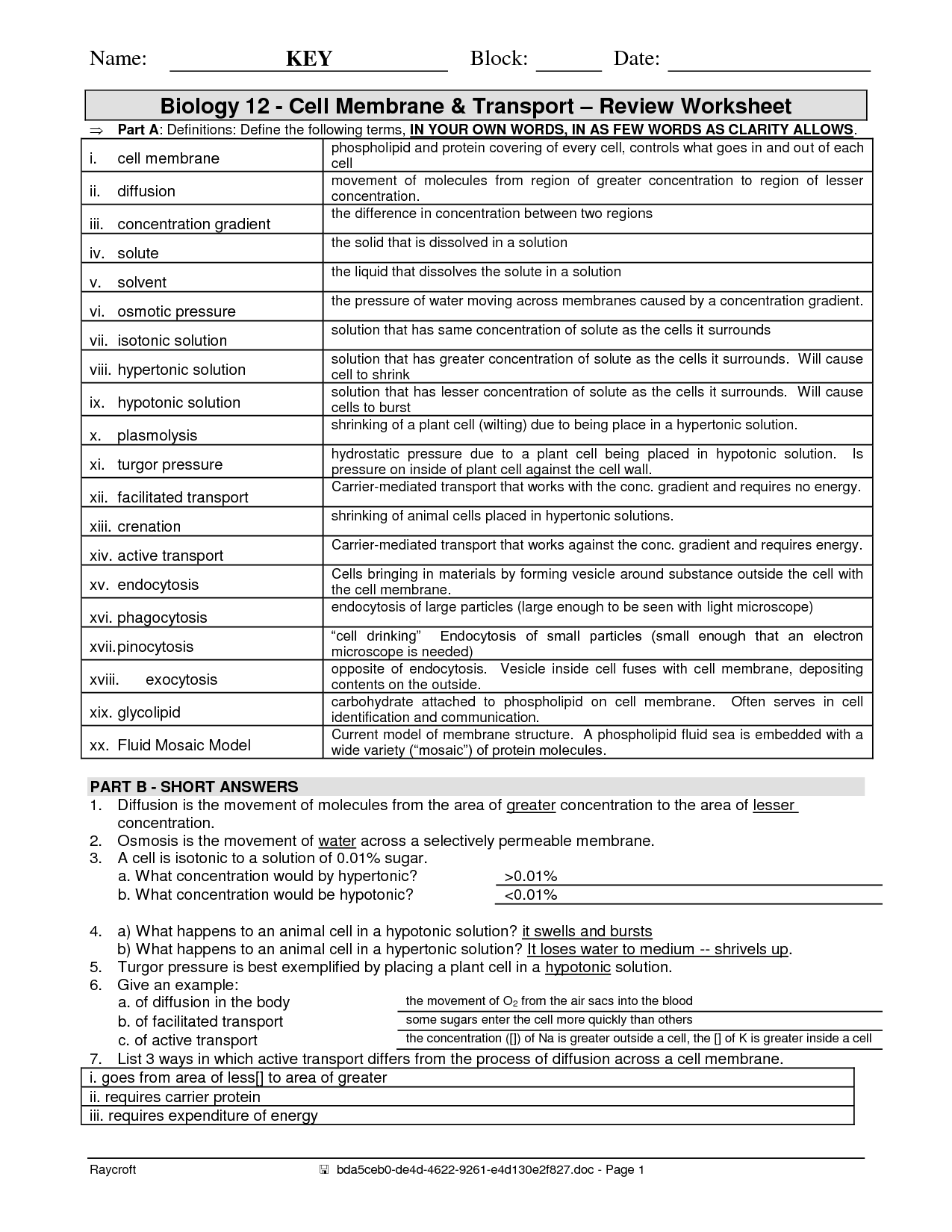
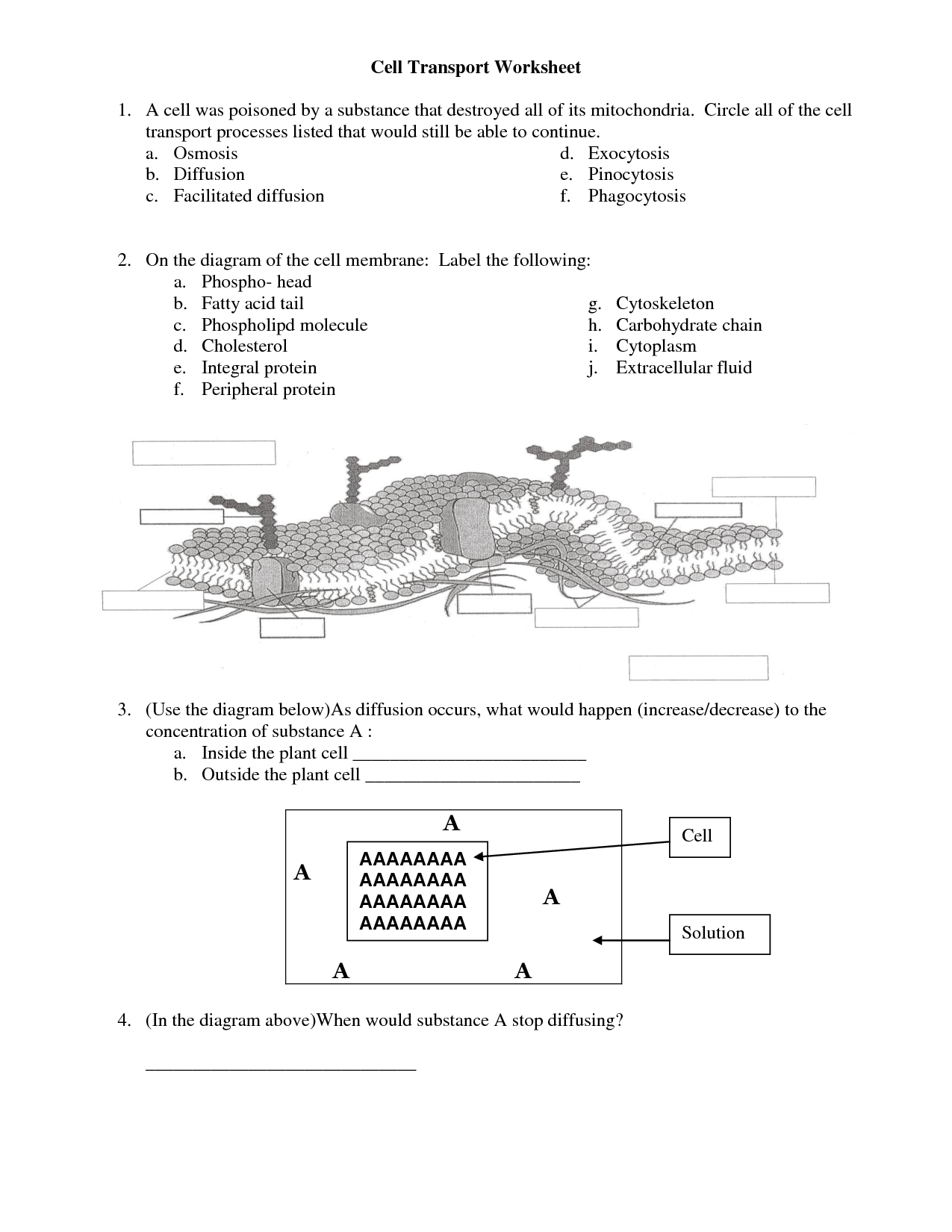
Before diving into the specific answers, it’s essential to recap the key concepts surrounding cellular transport. The cell membrane, composed primarily of a phospholipid bilayer, acts as a selective barrier. This barrier controls which molecules can pass through and how they do so. Cellular transport can be broadly categorized into two main types: passive transport and active transport.
Passive transport doesn’t require the cell to expend energy (ATP). This is because substances move down their concentration gradient – from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Examples of passive transport include:
- Simple Diffusion: The movement of molecules directly through the cell membrane. Typically involves small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Facilitated Diffusion: The movement of molecules across the cell membrane with the help of transport proteins (channel proteins or carrier proteins). This is necessary for larger or polar molecules like glucose and amino acids.
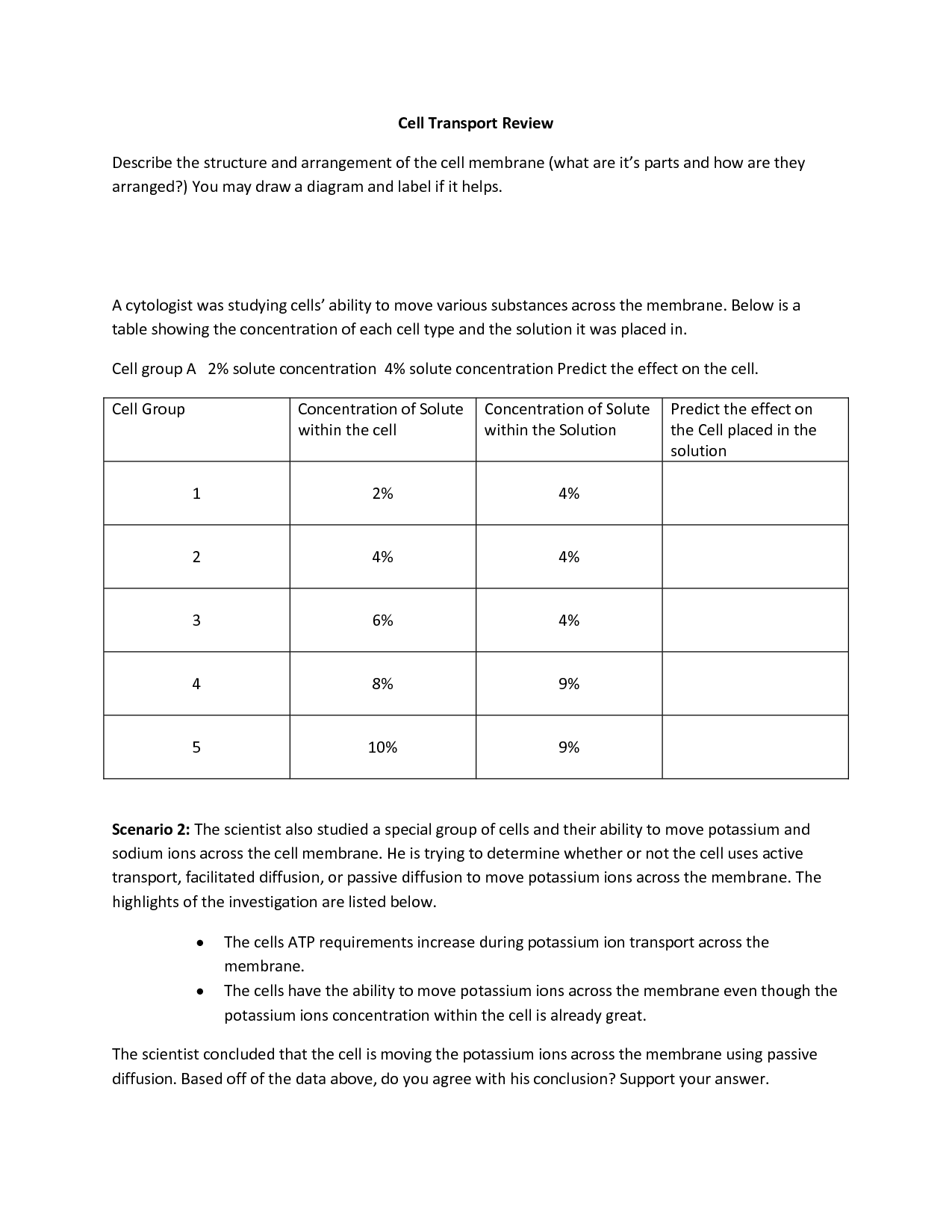
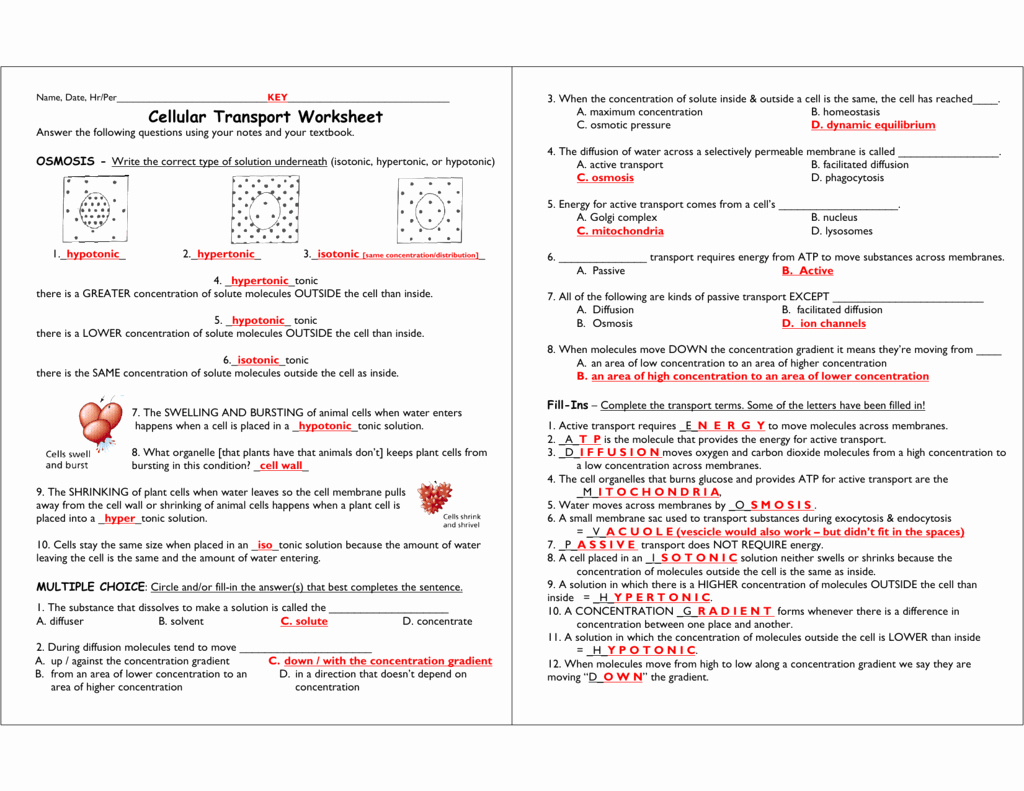
- Osmosis: The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration).
Active transport, on the other hand, requires the cell to expend energy, usually in the form of ATP. This is because substances are moved against their concentration gradient – from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Examples of active transport include:
- Primary Active Transport: Directly uses ATP to move substances across the membrane. A classic example is the sodium-potassium pump.
- Secondary Active Transport: Uses the electrochemical gradient created by primary active transport to move other substances across the membrane.
- Bulk Transport: Moves large molecules or large quantities of substances across the membrane through processes like endocytosis (bringing substances into the cell) and exocytosis (releasing substances from the cell). Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (cell eating) and pinocytosis (cell drinking).
Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers Explained
Now, let’s address the answers you might find in a typical Cellular Transport Worksheet. Remember that the specific questions and answers will vary depending on the worksheet, but this list covers many common scenarios.
Common Cellular Transport Worksheet Questions and Answers
-
Question: What is the main difference between passive and active transport?
- Answer: Passive transport does not require energy, while active transport requires energy (ATP).
-
Question: Define diffusion and give an example.
- Answer: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. An example is the movement of oxygen from the lungs into the blood.
-
Question: What type of transport is osmosis?
- Answer: Osmosis is a type of passive transport.
-
Question: Explain the role of transport proteins in facilitated diffusion.
- Answer: Transport proteins, such as channel proteins and carrier proteins, help specific molecules cross the cell membrane that cannot easily diffuse across the lipid bilayer due to their size or polarity.
-
Question: Describe the process of endocytosis.
- Answer: Endocytosis is a type of active transport where the cell membrane engulfs a substance and brings it into the cell in a vesicle.
-
Question: What is the function of the sodium-potassium pump, and is it active or passive transport?
- Answer: The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane by pumping sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and potassium ions (K+) into the cell. It is a type of active transport because it requires ATP.
-
Question: Distinguish between phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
- Answer: Phagocytosis is the engulfment of large particles or whole cells (“cell eating”), while pinocytosis is the engulfment of liquid droplets (“cell drinking”). Both are forms of endocytosis.
-
Question: How does the concentration gradient affect the direction of transport in passive transport?
- Answer: In passive transport, substances move down the concentration gradient, meaning they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement does not require energy input from the cell.
-
Question: Explain what happens to a red blood cell when placed in a hypotonic solution.
- Answer: In a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration than inside the cell), water will move into the red blood cell via osmosis. This causes the cell to swell and potentially burst (lyse).
-
Question: Explain what happens to a plant cell when placed in a hypertonic solution.
- Answer: In a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration than inside the cell), water will move out of the plant cell via osmosis. This causes the cell membrane to pull away from the cell wall (plasmolysis).
By understanding the fundamental principles and carefully reviewing these common questions and answers, you can confidently tackle any Cellular Transport Worksheet and build a solid foundation in cell biology. Remember to always check your textbook and lecture notes for further clarification on specific concepts. Good luck!
If you are looking for Cellular Transport Worksheet you’ve came to the right web. We have 20 Images about Cellular Transport Worksheet like Cell Transport Review Worksheet – Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers – E Street Light and also 16 The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology / worksheeto.com. Here it is:
Cellular Transport Worksheet
sahklubrad.com
16 The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology / Worksheeto.com
www.worksheeto.com
Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers – E Street Light

www.e-streetlight.com
Practice Types Of Cellular Transport Worksheet Answers – Printable Word

davida.davivienda.com
16 The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology / Worksheeto.com
www.worksheeto.com
22 22 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers% – E-streetlight.com

www.e-streetlight.com
Transport Across The Cell Membrane Worksheet Student Copy (3

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport Worksheet F2020 – Name

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Biology 1 – Cell Transport Overview Notes – Cell Transport Review

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Cellular Transport And The Cell Cycle Exercise Answer Key

worksheets.clipart-library.com
16 The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology / Worksheeto.com

www.worksheeto.com
Transport In Cells Worksheet Awesome Cellular Transport Worksheet
chessmuseum.org
22 22 Cell Transport Worksheet Answers% – Pro Worksheet

www.proworksheet.my.id
Reinforcement: Cell Structures And Functions With Labeling – Worksheets

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Cell Transport Worksheet Answers – Comprehensive Solutions For Biology

worksheets.clipart-library.com
SOLUTION: Cellular Transport Worksheet – Studypool

www.studypool.com
Cell Transport Review Worksheet – Fill Online, Printable, Fillable
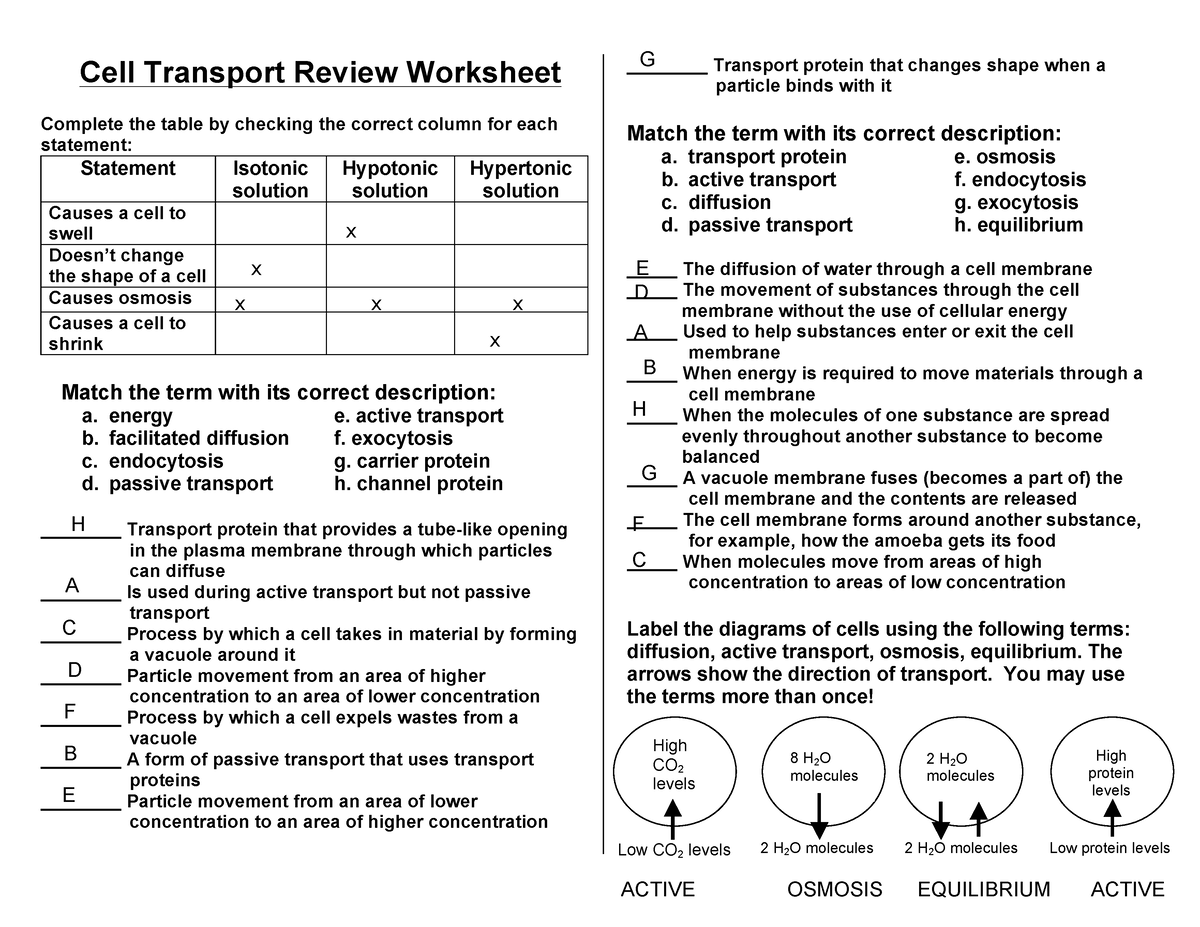
worksheets.clipart-library.com
Cell Transport Worksheet Answers – Owhentheyanks.com

www.owhentheyanks.com
Free Cellular Transport And The Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers, Download

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Cell Transport Worksheet Biology Answers – Owhentheyanks.com

www.owhentheyanks.com
Free cellular transport and the cell cycle worksheet answers, download …. 16 the 12 cell review worksheet answers biology / worksheeto.com. Cell transport worksheet biology answers – owhentheyanks.com