Understanding DNA mutations is a fundamental concept in biology, impacting everything from evolution to the development of diseases like cancer. Practice worksheets are often used to solidify this understanding, allowing students to apply their knowledge and identify different types of mutations. However, grasping these concepts and accurately answering worksheet questions can sometimes be challenging. Many students find themselves searching for “DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answers” to check their work, understand the rationale behind the correct answers, and identify areas where they need further study. This post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the types of DNA mutations typically covered in practice worksheets, alongside a possible answer key and explanations to help you master this critical topic.
Types of DNA Mutations
Before diving into potential answers to a practice worksheet, it’s important to review the different types of DNA mutations. These mutations can occur spontaneously during DNA replication or be induced by external factors such as radiation or chemicals. They are generally categorized as point mutations or frameshift mutations.
Point Mutations
Point mutations involve a change in a single nucleotide base pair within the DNA sequence. There are three main types of point mutations:
- Substitution: One nucleotide is replaced by another. Substitutions can be further classified as:
- Silent Mutation: The substitution does not change the amino acid sequence of the protein. This often occurs because multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
- Missense Mutation: The substitution results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the protein. This can have varying effects on protein function, ranging from negligible to severe.
- Nonsense Mutation: The substitution creates a premature stop codon, resulting in a truncated (shortened) protein. This usually leads to a non-functional protein.
Frameshift Mutations
Frameshift mutations occur when nucleotides are either inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence. These insertions or deletions shift the reading frame, altering the sequence of amino acids downstream of the mutation. Because the ribosome reads the genetic code in triplets (codons), adding or removing a number of nucleotides that is not a multiple of three will disrupt the reading frame.
- Insertion: One or more nucleotides are added to the DNA sequence.
- Deletion: One or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence.
Frameshift mutations often have more drastic consequences than point mutations, as they can significantly alter the protein’s structure and function, leading to a completely different and often non-functional protein.
DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answers (Example)
Below is a sample answer key to a hypothetical DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet. Note that the specific questions and answers will vary depending on the content of your particular worksheet. This is meant to be a guide to understanding the concepts.
-
Question: Identify the type of mutation in the following sequence:
Original Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAGCTAG-3′
Mutated Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAGCTAG-3′ (Assume this represents a replication error where the sequence is identical).
Answer: No mutation. The sequence is identical to the original. -
Question: Identify the type of mutation in the following sequence:
Original Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAGCTAG-3′
Mutated Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTGGCTAG-3′
Answer: Substitution (specifically, a missense mutation if this results in a different amino acid). The ‘A’ at position 7 has been replaced with a ‘G’. -
Question: Identify the type of mutation in the following sequence:
Original Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAGCTAG-3′
Mutated Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAAGCTAG-3′
Answer: Insertion. An ‘A’ has been inserted after ‘GTA’. This is a frameshift mutation. -
Question: Identify the type of mutation in the following sequence:
Original Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTAGCTAG-3′
Mutated Sequence: 5′-ATGCGTCTAG-3′
Answer: Deletion. ‘AGC’ has been deleted. This is a frameshift mutation. -
Question: Original DNA sequence codes for the following mRNA sequence: AUG-CCU-GAA-UAG. A mutation occurs resulting in the mRNA sequence AUG-CCU-UAA-UAG. What type of mutation is this and what is the likely effect?
Answer: This is a nonsense mutation. The codon GAA (Glutamic Acid) has been changed to UAA (Stop codon). This will likely result in a truncated and non-functional protein. -
Question: Explain the difference between a missense and a nonsense mutation.
Answer: A missense mutation is a point mutation where a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation is a point mutation where a single nucleotide change results in a premature stop codon. Missense mutations result in a different amino acid being incorporated into the protein, whereas nonsense mutations result in a shortened, often non-functional protein.
By carefully analyzing the original and mutated sequences, and considering the different types of mutations, you can effectively tackle DNA Mutations practice worksheets. Remember to pay close attention to the reading frame and the potential consequences of each mutation on the resulting protein. Consistent practice and a solid understanding of the underlying principles will help you master this important concept.
If you are searching about DNA – Definition, Function, Structure and Discovery | Biology Dictionary you’ve came to the right page. We have 20 Pictures about DNA – Definition, Function, Structure and Discovery | Biology Dictionary like DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, and Mutation, DNA Structure | Visual.ly and also Colorful human DNA strand surrounded, DNA structure, 22379220 Stock. Here you go:
DNA – Definition, Function, Structure And Discovery | Biology Dictionary

biologydictionary.net
Digital Illustration Of A Dna

www.setaswall.com
DNA Facts And Information

www.nationalgeographic.com
What Is DNA? | Live Science

www.livescience.com
DNA: Definition, Structure And Functions | Healthtian

healthtian.com
DNA Structure Isolated Background 3d Illustration 18871969 PNG

www.vecteezy.com
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Struktur, Fungsi, Dan Kelainan DNA
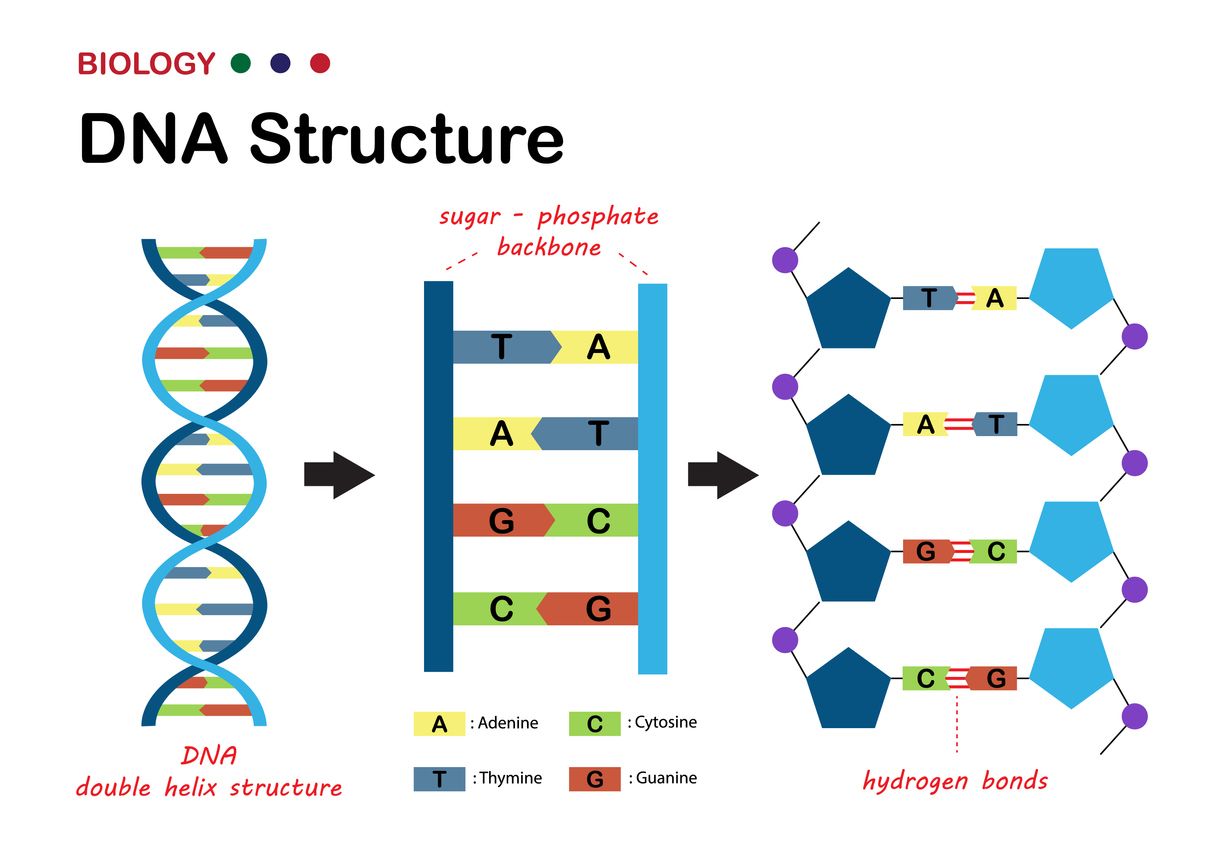
www.haibunda.com
DNA | Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure

www.britannica.com
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model

alevelbiology.co.uk
DNA Definition And Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-476980521-56a134e65f9b58b7d0bd059b.jpg)
www.thoughtco.com
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
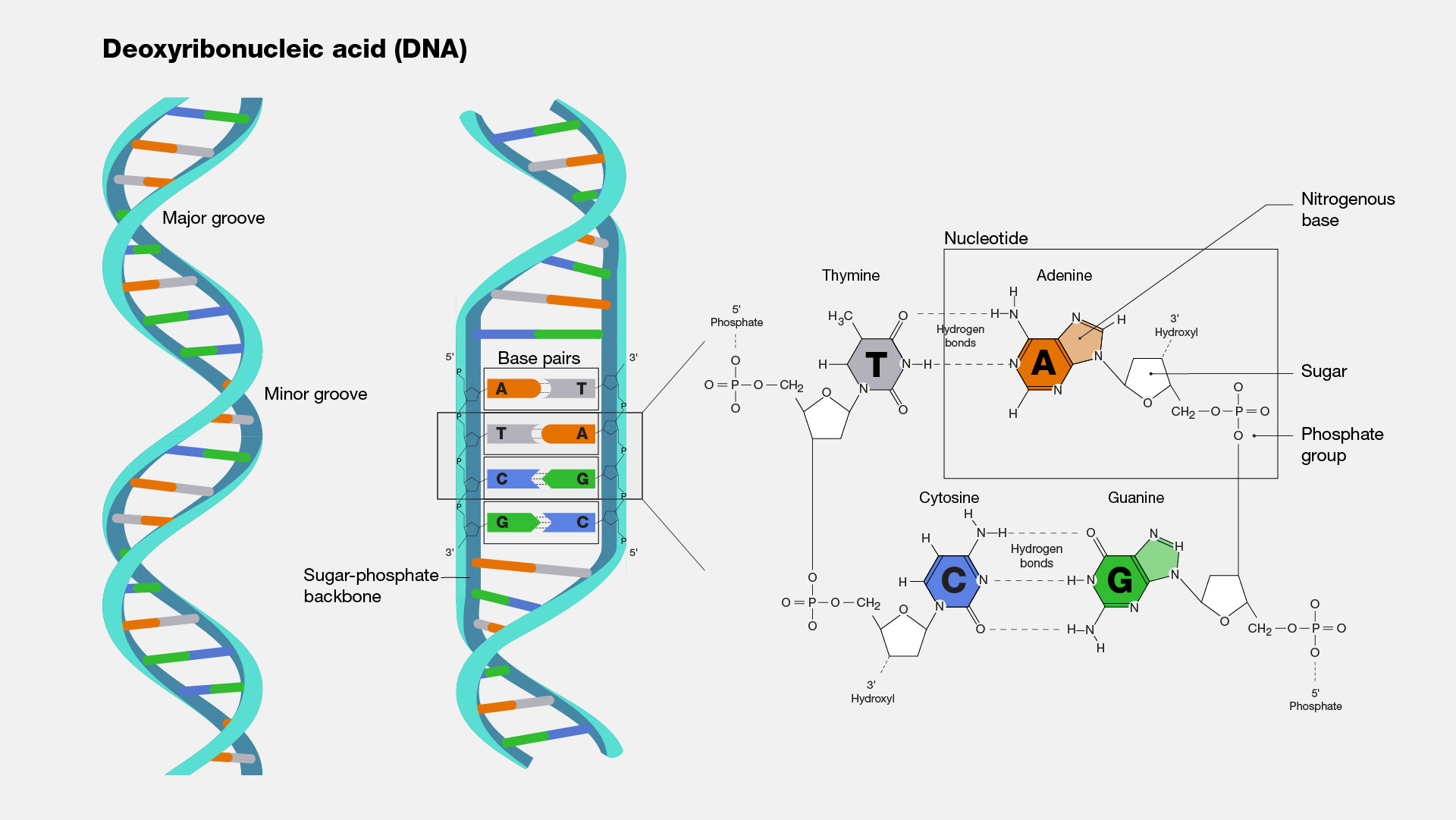
www.genome.gov
DNA Definition: Shape, Replication, And Mutation
/3-D_DNA-56a09ae45f9b58eba4b20266.jpg)
www.thoughtco.com
What Does DNA Stand For, And How Does It Work? | Extremetech

www.extremetech.com
DNA Structure | Visual.ly

visual.ly
DNA | Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure

www.britannica.com
What Is DNA? – Definition, Structure, Types, Functions – GeeksforGeeks

www.geeksforgeeks.org
3d Structure Of Dna Model

ar.inspiredpencil.com
DNA Structure Model On White Stock Photo – Alamy

www.alamy.com
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model

alevelbiology.co.uk
Colorful Human DNA Strand Surrounded, DNA Structure, 22379220 Stock
www.vecteezy.com
Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). What does dna stand for, and how does it work?. dna facts and information
