Understanding genetic mutations is fundamental to grasping the mechanisms of evolution, disease, and inheritance. Worksheets designed to reinforce these concepts are valuable tools for students, but sometimes understanding the answers can be a hurdle. This post aims to provide a clear and comprehensive answer key to a typical genetic mutation worksheet, along with explanations to aid in deeper comprehension. The goal is not simply to give you the answers, but to help you understand *why* those are the answers.
Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
Below is a sample answer key, assuming a worksheet covering common mutation types and their consequences. The exact questions and answers will vary depending on your specific worksheet, so remember to use this as a guide to understanding, not just a copy-paste solution.
Part 1: Identifying Mutation Types
- Question 1: The original DNA sequence is ATG-CGA-TTC and the mutated sequence is ATG-CGA-TGT. Identify the type of mutation.
- Answer: Substitution (specifically, a transversion if focusing on purine/pyrimidine changes)
- Explanation: A single nucleotide base has been replaced (C with G) without altering the overall reading frame. This is a classic substitution. Transversion refers to replacing a purine with a pyrimidine or vice versa.
- Question 2: The original DNA sequence is GGC-ATT-AGC and the mutated sequence is GGCA-TTA-GC. Identify the type of mutation.
- Answer: Deletion (specifically, a frame-shift deletion)
- Explanation: The ‘T’ from “ATT” has been removed, shifting the entire reading frame downstream. This significantly alters the amino acid sequence that will be translated.
- Question 3: The original DNA sequence is TTA-GGC-CAT and the mutated sequence is TTA-GGG-CCA-T. Identify the type of mutation.
- Answer: Insertion (specifically, a frame-shift insertion)
- Explanation: An extra ‘G’ has been added, shifting the reading frame. Like deletion, this type of mutation usually has a drastic effect on the resulting protein.
- Question 4: The original DNA sequence is CCC-GGG-AAA and the mutated sequence is CCC-GGG-AAA. Identify the type of mutation.
- Answer: No mutation.
- Explanation: The sequences are identical, so there’s no mutation present. This is a trick question to ensure students are carefully comparing sequences.
- Question 5: The original DNA sequence is AAA-TTT-CCC and the mutated sequence is AAA-TAT-CCC. Identify the type of mutation.
- Answer: Substitution (Transition)
- Explanation: ‘T’ has been substituted for another ‘T’. Even though the overall amino acid might be the same due to the redundancy of the genetic code, it still represents a change at the DNA level. Transition involves substitution within the same type of base (purine to purine or pyrimidine to pyrimidine).
Part 2: Consequences of Mutations
- Question 1: A mutation results in a premature stop codon. What is the likely consequence for the protein?
- Answer: The protein will likely be truncated (shorter than normal) and non-functional.
- Explanation: A premature stop codon signals the ribosome to stop translation early. This results in a shortened protein lacking essential amino acids, rendering it useless or even harmful.
- Question 2: A mutation changes a codon from GGC (Glycine) to GGG (Glycine). What is the likely consequence for the protein?
- Answer: This is likely a silent mutation, meaning there will be no change to the protein.
- Explanation: The genetic code is redundant, meaning that multiple codons can code for the same amino acid. Since both GGC and GGG code for glycine, the protein sequence remains unchanged.
- Question 3: A frame-shift mutation occurs near the beginning of a gene. What is the likely consequence for the protein?
- Answer: The protein will likely be significantly altered and non-functional. The further upstream (closer to the start) the mutation occurs, the greater the impact.
- Explanation: Frame-shift mutations disrupt the reading frame for all codons downstream of the mutation. This leads to a completely different amino acid sequence, resulting in a protein with drastically altered structure and function.
- Question 4: A mutation occurs in a non-coding region of DNA. What is the likely consequence?
- Answer: The consequence is variable and depends on the specific non-coding region. It may have no effect, or it could affect gene regulation (e.g., transcription).
- Explanation: While non-coding regions don’t directly code for proteins, some play crucial roles in gene expression. Mutations in promoter regions, enhancers, or silencers can significantly alter how much of a protein is produced. Other non-coding regions might have no known function, so mutations there are unlikely to have any noticeable effect.
- Question 5: A mutation results in an amino acid change in the active site of an enzyme. What is the likely consequence?
- Answer: The enzyme’s activity will likely be impaired or abolished.
- Explanation: The active site is the region of an enzyme where substrates bind and catalysis occurs. A change in the amino acid sequence in this region can disrupt substrate binding or the catalytic mechanism, rendering the enzyme less effective or completely non-functional.
This answer key provides a basic understanding of genetic mutations. Remember that real-world mutations can be much more complex and their consequences often depend on multiple factors, including the specific gene affected, the location of the mutation within the gene, and the individual’s genetic background. Always consult your textbook or instructor for more detailed information and specific examples relevant to your course.
If you are searching about English worksheets: Celebrity Genetics – Worksheets Library you’ve visit to the right page. We have 20 Images about English worksheets: Celebrity Genetics – Worksheets Library like Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer Key – Key Worksheet, Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key – E-streetlight.com and also Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer. Here you go:
English Worksheets: Celebrity Genetics – Worksheets Library

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Mutation Worksheet 2 Answer Key
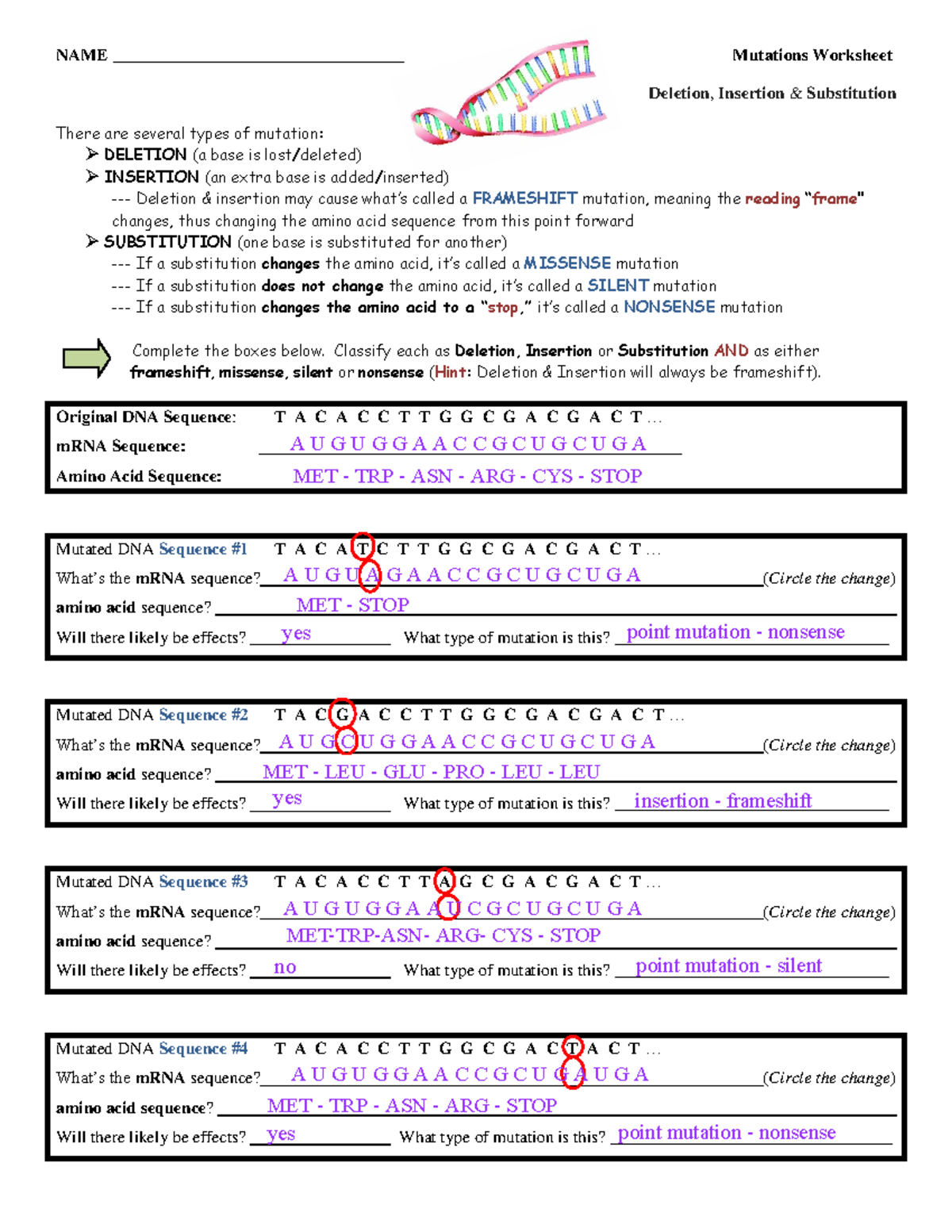
oraclenotepadr1schematic.z21.web.core.windows.net
Mutationspglguigiugu – Genetic Mutations 1 Genetic Mutations What

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Genetic Mutation Worksheet

studyschoolsgraffito.z21.web.core.windows.net
SOLUTION: Gene Mutations Worksheet – Answer Key – Studypool

worksheets.clipart-library.com
X Men Genetic Mutations Worksheet Answer Key – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
SOLUTION: Mutations Practice – Studypool – Worksheets Library

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Genetics Worksheets And Printables – Worksheets Library
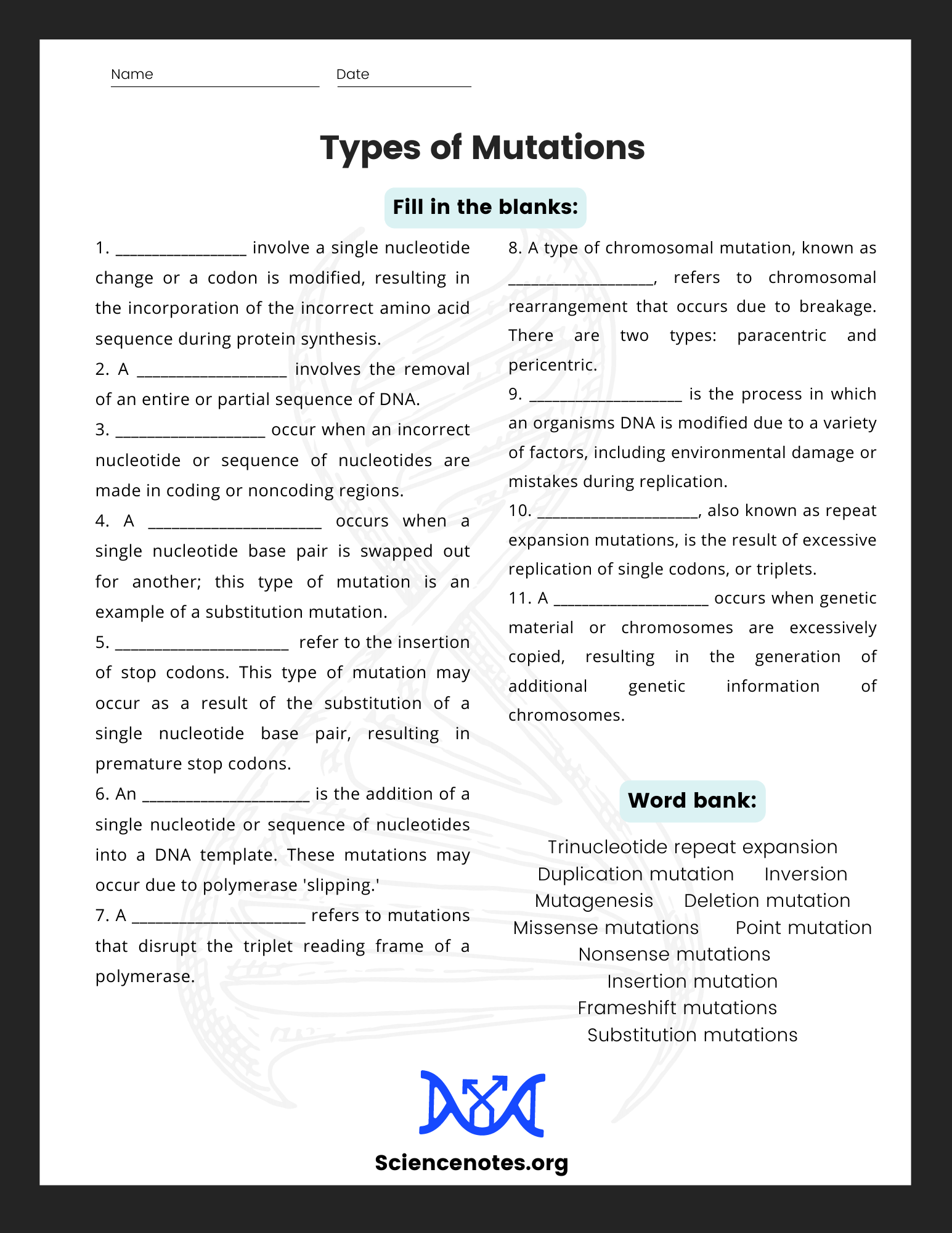
worksheets.clipart-library.com
Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answers | Exercises

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer Key – Key Worksheet
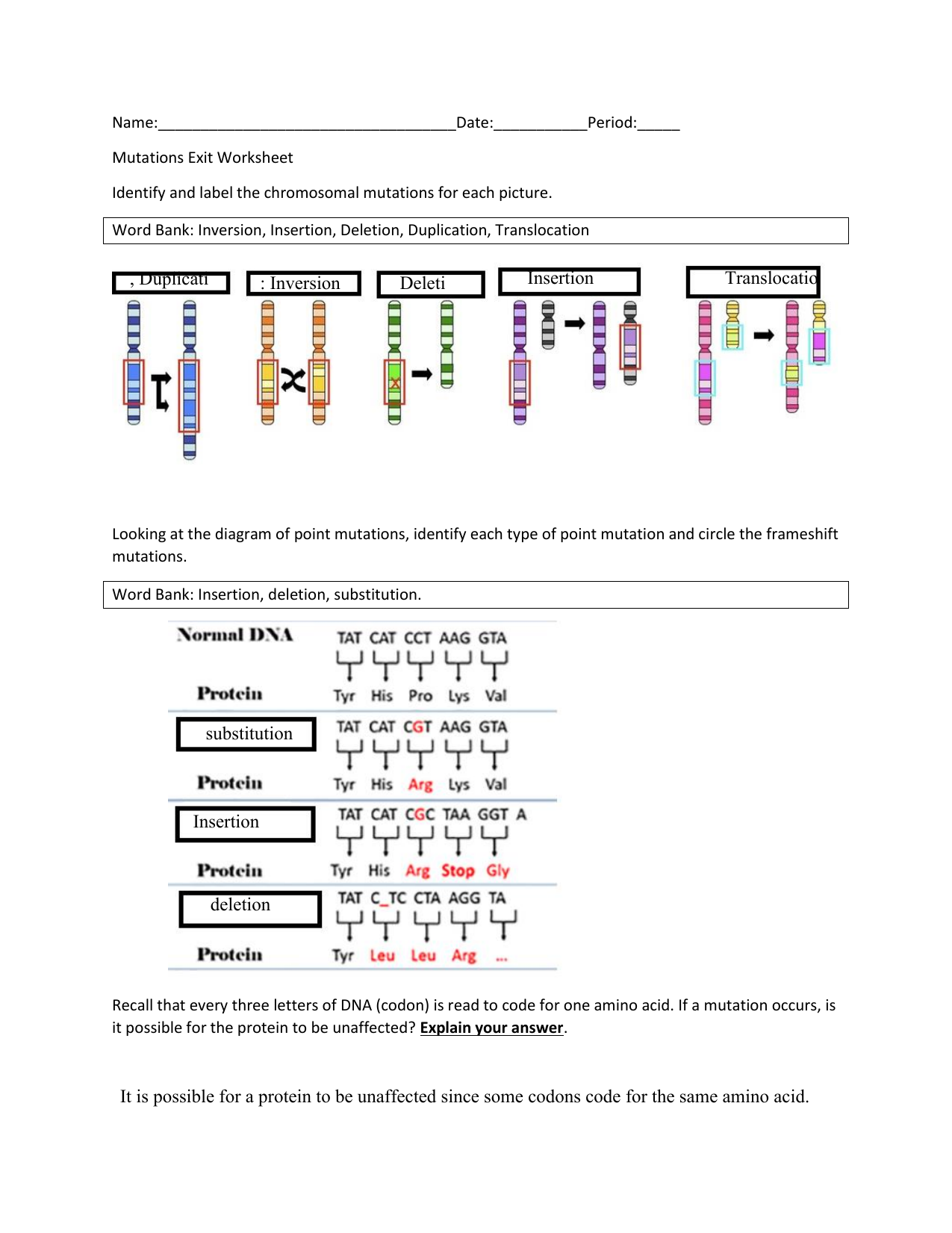
keyworksheet.info
Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer
lessonschoolswealed.z5.web.core.windows.net
Mutation Worksheet Answer Key Biology
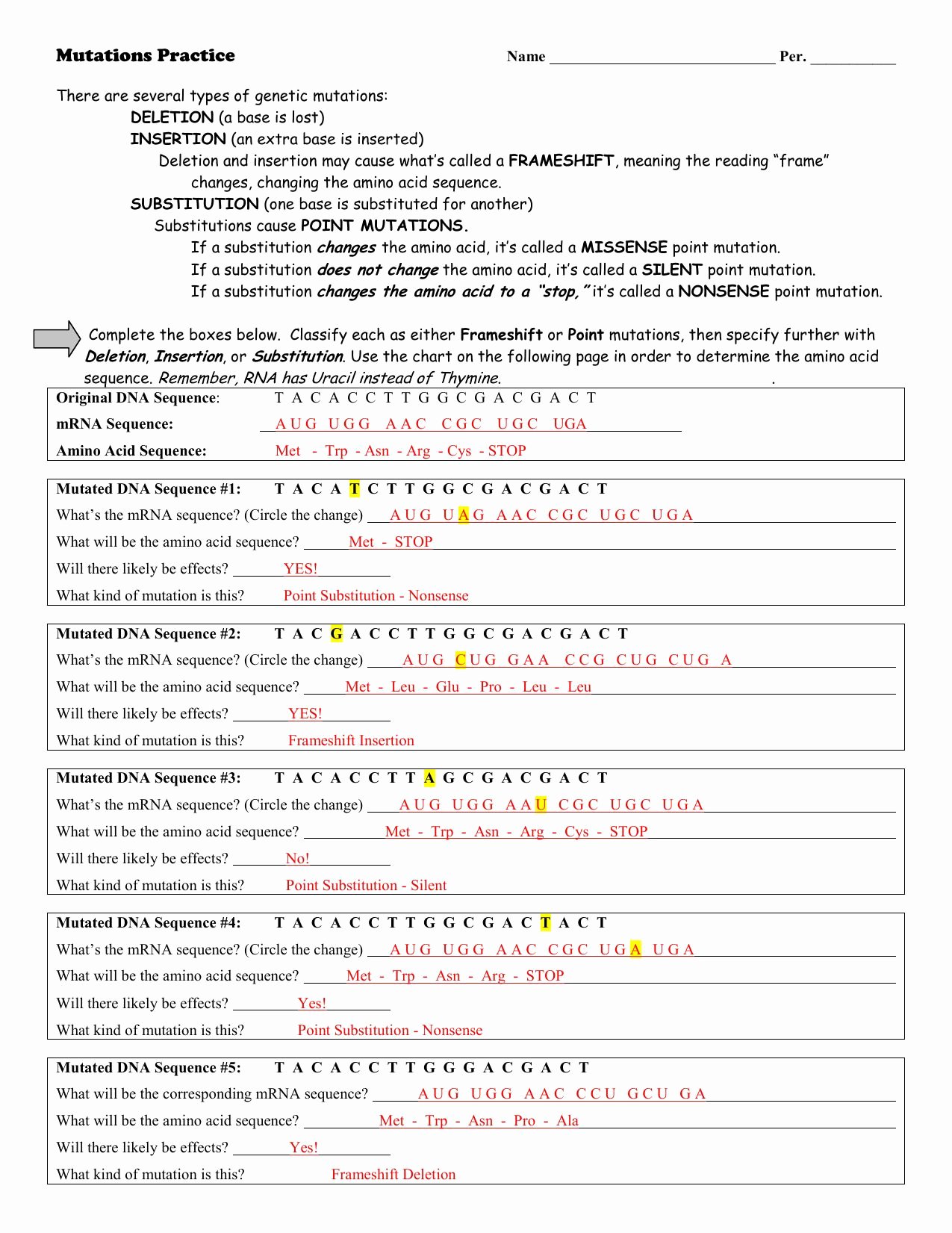
learningzonemeisturumps.z21.web.core.windows.net
Mutations Worksheet Answer Key – Fill Online, Printable, Fillable

worksheets.clipart-library.com
DNA Mutation Simulation Worksheet – Bio 101 Activities – Studocu

www.studocu.com
SOLUTION: Gene Mutations Worksheet – Answer Key – Studypool

worksheets.clipart-library.com
13 Human Variations Worksheet / Worksheeto.com

www.worksheeto.com
Dna Mutations Worksheet Answer Key – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key – E-streetlight.com

www.e-streetlight.com
Gene And Chromosome Mutation Worksheet – E-streetlight.com

www.e-streetlight.com
Dividing Polynomials Worksheet Answers Worksheet For Education – Artofit

www.artofit.org
Gene and chromosome mutation worksheet – e-streetlight.com. genetic mutation worksheet. Solution: gene mutations worksheet