Understanding osmosis and tonicity can seem daunting at first, but it’s a crucial concept in biology, particularly when studying cell function and fluid balance. Whether you’re a high school student prepping for a biology exam, a college student tackling physiology, or just someone curious about how cells work, grasping these principles is essential. This post aims to clarify these concepts and provide you with resources to test your knowledge. One such resource is an Osmosis and Tonicity worksheet, which allows you to apply your understanding through problem-solving.
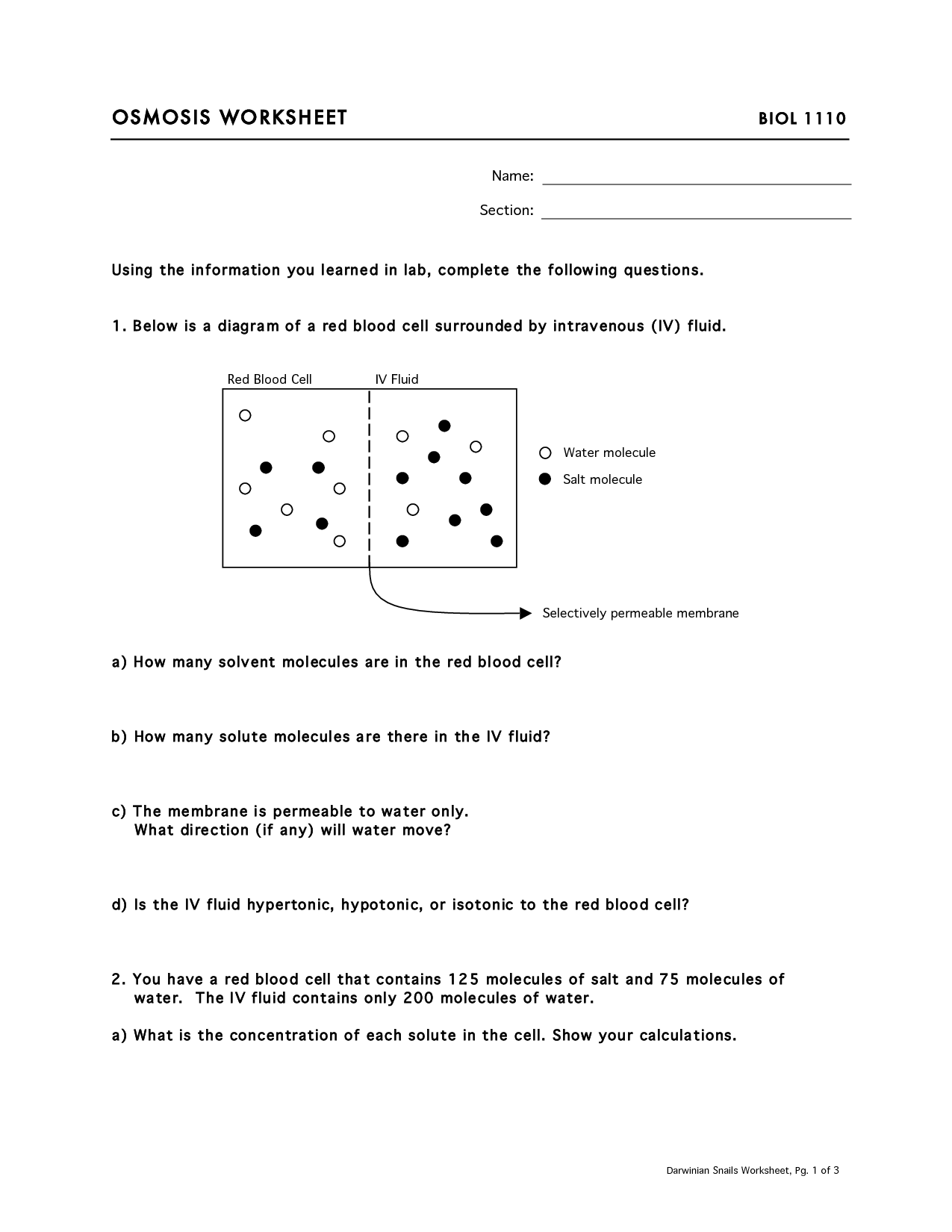
Osmosis, in its simplest form, is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. This movement continues until the water concentration on both sides of the membrane is equal. The driving force behind osmosis is the difference in solute concentration, often referred to as osmotic pressure. It’s vital to remember that osmosis is *only* about water; solutes themselves don’t pass through the membrane (in typical osmosis scenarios).
Tonicity, on the other hand, describes the relative concentration of solutes dissolved in a solution compared to another solution, specifically within a cell. This difference in solute concentration dictates the direction of water movement (osmosis). Tonicity is a *relative* term; we always compare the solute concentration of one solution to another. We use three key terms to describe tonicity: hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic.
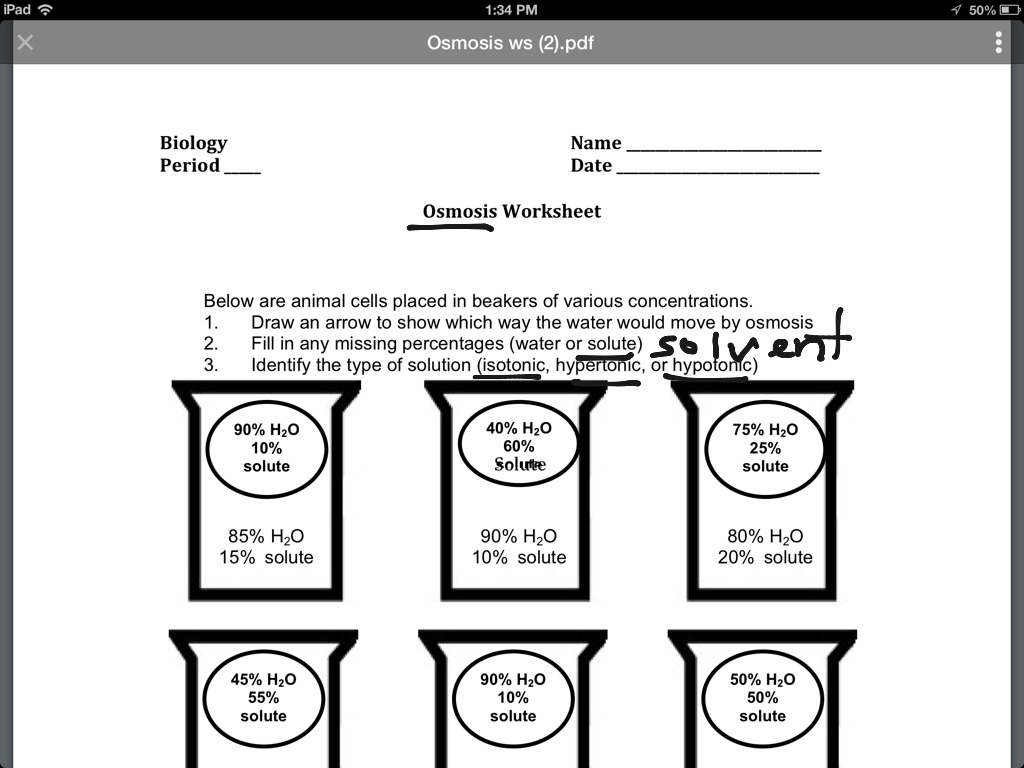
A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell’s interior. This means water will move *out* of the cell and into the surrounding solution, causing the cell to shrink (crenation in animal cells; plasmolysis in plant cells). A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell’s interior. Water will move *into* the cell, causing it to swell and potentially burst (lyse) in animal cells. In plant cells, the cell wall prevents bursting, but the cell becomes turgid. Finally, an isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as the cell’s interior. There is no net movement of water, and the cell maintains its normal shape.
Many Osmosis and Tonicity worksheets will present scenarios involving different solute concentrations and ask you to predict the direction of water movement and the resulting effect on the cell. Mastering these concepts requires practice and a clear understanding of the definitions. If you find yourself struggling, consider reviewing your textbook, watching online tutorials, or working through practice problems with a study group.
Osmosis and Tonicity Worksheet Answers & Explanations
Below are answers to some typical Osmosis and Tonicity worksheet questions. This is meant as a guide and not a substitute for understanding the underlying principles. Remember to always try to solve the problems yourself first!
Example Scenario 1: Red Blood Cell in Different Solutions
- Question: A red blood cell is placed in a solution with 10% NaCl. The cell’s internal NaCl concentration is 0.9%. What will happen to the cell? Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to the cell?
- Answer:
- Tonicity: The solution is hypertonic to the cell.
- Water Movement: Water will move out of the cell.
- Effect on Cell: The cell will shrink (crenate).
Example Scenario 2: Plant Cell in Distilled Water
- Question: A plant cell is placed in distilled water (pure water). What will happen to the cell? Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to the cell?
- Answer:
- Tonicity: The solution is hypotonic to the cell.
- Water Movement: Water will move into the cell.
- Effect on Cell: The cell will become turgid (swollen, but not bursting due to the cell wall).
Example Scenario 3: Animal Cell in 0.9% Saline
- Question: An animal cell is placed in a 0.9% saline (NaCl) solution. The cell’s internal NaCl concentration is also 0.9%. What will happen to the cell? Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to the cell?
- Answer:
- Tonicity: The solution is isotonic to the cell.
- Water Movement: There will be no net movement of water.
- Effect on Cell: The cell will maintain its normal shape.
Example Scenario 4: Predicting Water Potential
- Question: Solution A has a solute potential of -0.8 MPa and a pressure potential of +0.5 MPa. Solution B has a solute potential of -0.3 MPa and a pressure potential of +0.2 MPa. Which direction will water move?
- Answer:
- Calculate Water Potential: Water potential is calculated by adding solute potential and pressure potential.
- Solution A water potential: -0.8 MPa + 0.5 MPa = -0.3 MPa
- Solution B water potential: -0.3 MPa + 0.2 MPa = -0.1 MPa
- Water Movement: Water will move from Solution B (higher water potential) to Solution A (lower water potential).
These examples should provide a good starting point for tackling Osmosis and Tonicity worksheets. Remember to carefully analyze each scenario, identify the relative solute concentrations, and predict the direction of water movement. Good luck!
If you are looking for Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet – Worksheets For Kindergarten you’ve came to the right page. We have 20 Images about Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet – Worksheets For Kindergarten like Osmosis and tonicity Worksheet Inspirational Osmosis and tonicity, Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet – E-streetlight.com and also Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet – Worksheets For Kindergarten. Here you go:
Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet – Worksheets For Kindergarten
worksheets.ekocraft-appleleaf.com
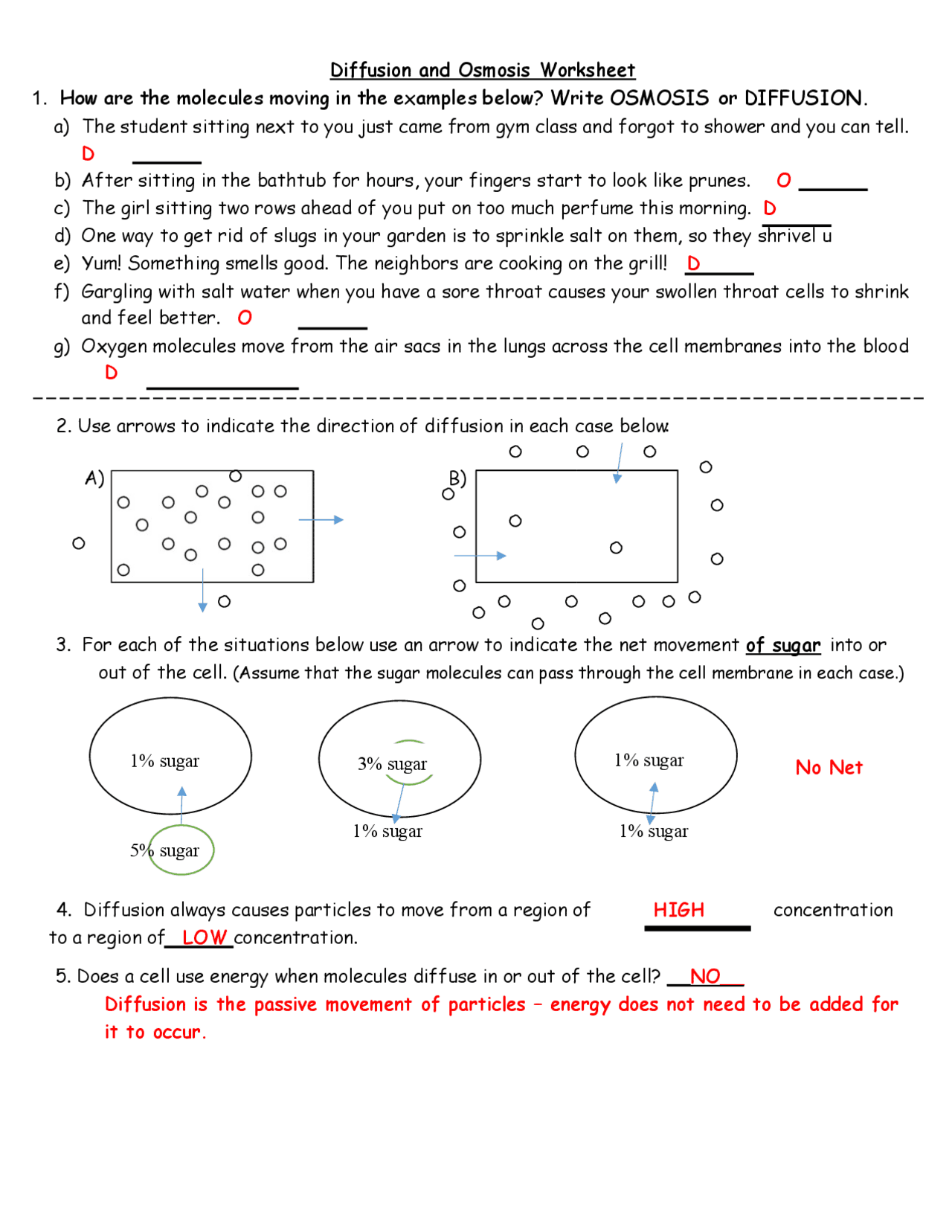
Diffusion & Osmosis Worksheet ANSWERS | Exams Biological Sciences
worksheets.clipart-library.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet Answers – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
Topic – Osmosis | ShowMe Online Learning – Worksheets Library
worksheets.clipart-library.com
Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key – Printable Word Searches
davida.davivienda.com
17 Osmosis Worksheet Answers – Free PDF At Worksheeto.com

www.worksheeto.com
SOLUTION: Cell Membrane Tonicity Worksheet – Studypool – Worksheets Library

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
Copy Of Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet – Name Alaxia Baldwin Cell

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet – E-streetlight.com
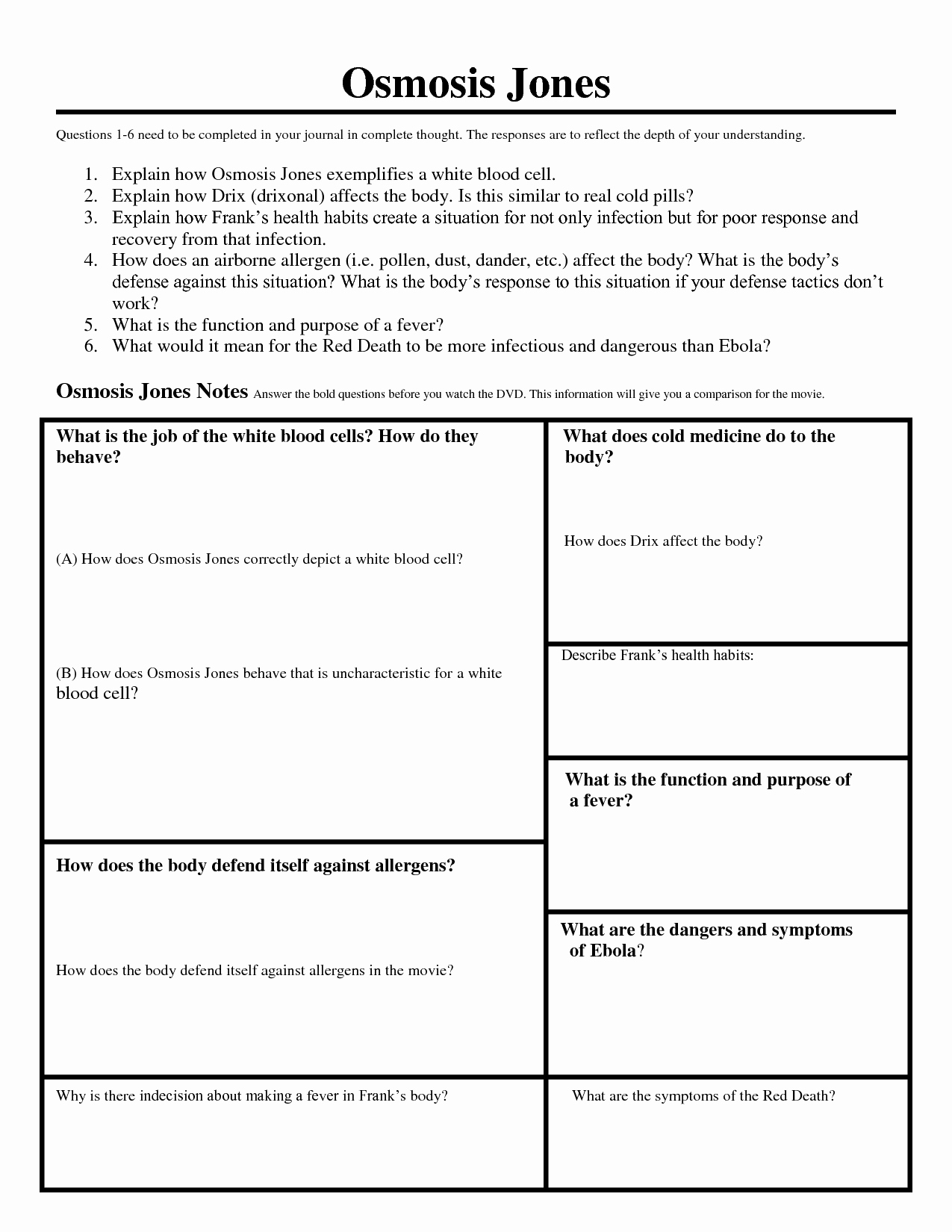
www.e-streetlight.com
Osmosis Worksheet – Flying Colors Science – Worksheets Library

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport Worksheet F2020 – Name

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet – E-streetlight.com

www.e-streetlight.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet – E-streetlight.com

www.e-streetlight.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet Unique 48 Tonicity And Osmosis Worksheet

chessmuseum.org
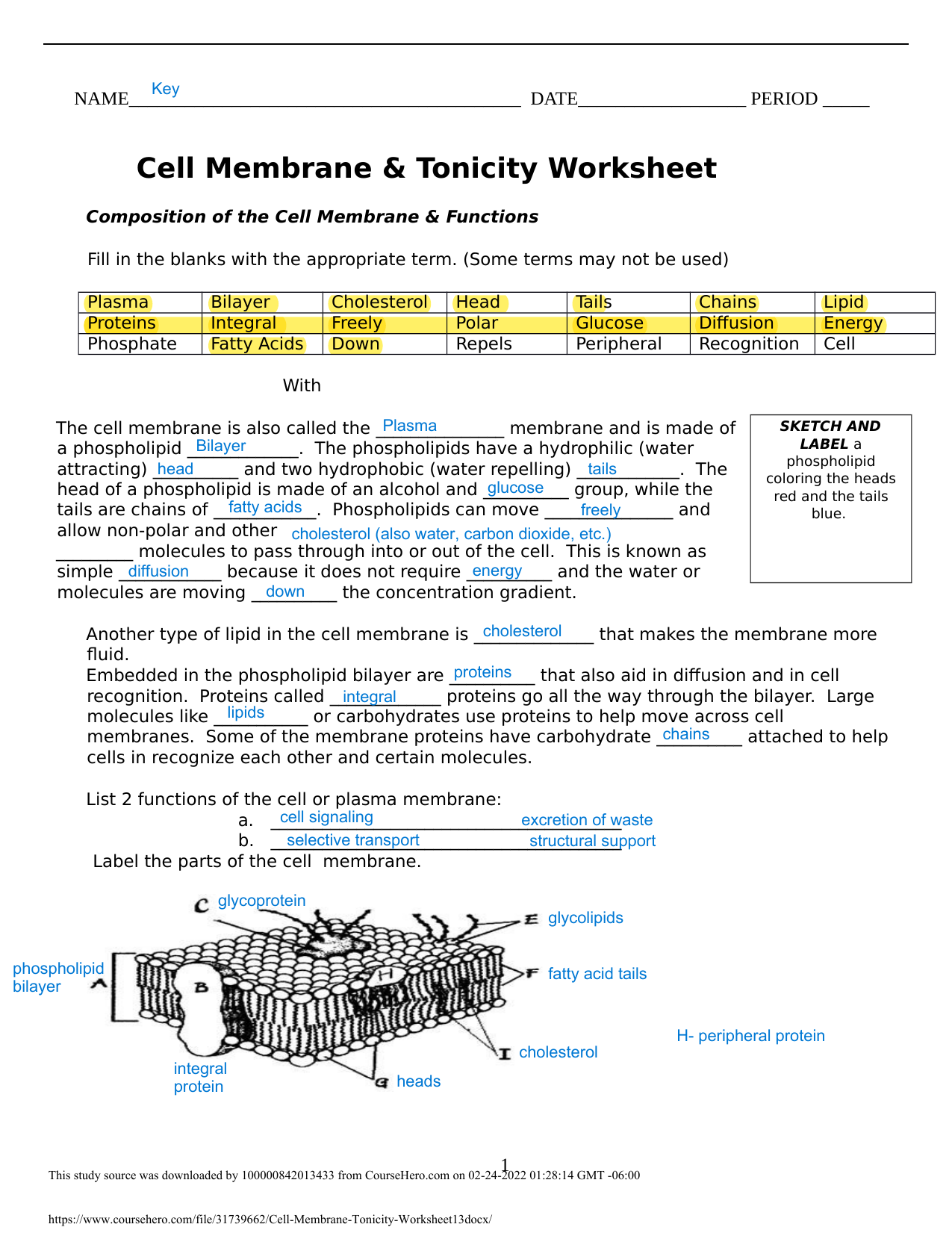
Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet Answers 1 1 .docx – NAME DATE

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet Inspirational Osmosis And Tonicity

chessmuseum.org
Osmosis And Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
Cell Membrane And Tonicity Worksheet – Owhentheyanks.com
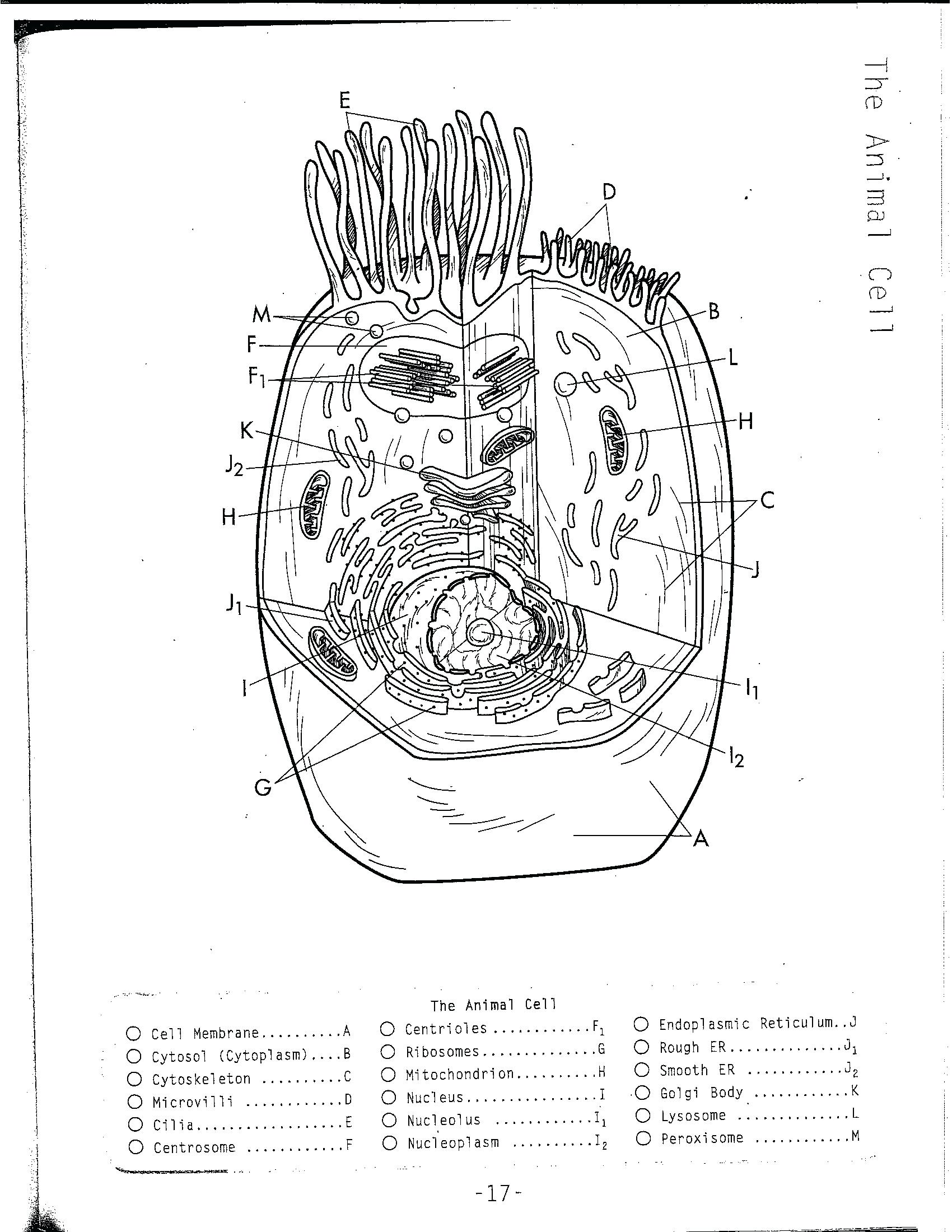
www.owhentheyanks.com
SOLUTION: Cell Membrane Tonicity Worksheet – Studypool – Worksheets Library

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Copy of tonicity and osmosis worksheet. osmosis and tonicity worksheet answers. osmosis and tonicity worksheet inspirational osmosis and tonicity …