Navigating the complex world of evolution can sometimes feel like wading through a dense jungle. One of the most crucial concepts to grasp is natural selection, the engine driving evolutionary change. But natural selection isn’t a monolithic force; it manifests in various forms, each shaping populations in distinct ways. A fantastic tool for understanding these diverse expressions is a well-designed “Types of Natural Selection Worksheet.” These worksheets often present scenarios and ask students to identify the specific type of selection at play. But simply filling in the blanks isn’t enough. True understanding requires a deeper dive into the underlying principles and the specific ecological pressures that lead to each type.
This post aims to clarify the different types of natural selection commonly explored in these worksheets and provide a framework for correctly identifying them. We’ll cover directional selection, stabilizing selection, disruptive selection, and, briefly, balancing selection. Think of this as your comprehensive guide to acing those natural selection worksheet challenges!
Understanding the Core Types of Natural Selection
The foundation of natural selection lies in the observation that individuals within a population exhibit variations in their traits. Some of these variations are heritable, meaning they can be passed down from parents to offspring. When the environment favors certain traits over others, individuals with those advantageous traits are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass on their genes. This leads to a shift in the population’s genetic makeup over time. The way this shift occurs depends on the specific selective pressures.
Directional Selection
Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored over all others. Imagine a population of birds where beak size varies. If the only available food source becomes hard seeds, birds with larger, stronger beaks will be better equipped to crack them open and survive. Over generations, the average beak size within the population will shift towards the larger end of the spectrum. This type of selection essentially pushes the population in one direction along the phenotypic range.
Common examples include the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria (where resistant strains are favored when antibiotics are present) and the peppered moth during the Industrial Revolution (where darker moths were favored in soot-covered environments).
Stabilizing Selection
Stabilizing selection favors intermediate phenotypes and selects against extreme variations. Consider human birth weight. Babies that are too small are vulnerable to health complications, while babies that are too large can lead to difficult and dangerous deliveries. The optimal birth weight is somewhere in the middle. Stabilizing selection reduces the variation in the population, keeping the trait close to the existing average.
Another example is the clutch size of birds. Too few eggs may result in low reproductive success, while too many eggs may result in the parents being unable to provide sufficient resources for all the offspring.
Disruptive Selection
Disruptive selection, also known as diversifying selection, favors both extreme phenotypes and selects against intermediate values. This can lead to the formation of two or more distinct subgroups within a population. Picture a population of birds with beaks that vary in size. If the available food sources are only very large seeds or very small insects, birds with either very large or very small beaks will be favored. Birds with intermediate beak sizes, unable to efficiently handle either food source, will be at a disadvantage.
A classic example involves the African black-bellied seedcracker finch. These finches have either large, powerful beaks to crack hard seeds, or small, nimble beaks to handle small, soft seeds. Intermediate beak sizes are less efficient, leading to a bimodal distribution of beak sizes within the population.
Worksheets may include images or scenarios describing a population over generations. Look for trends and shifts in the trait distribution to identify the type of selection.
Balancing selection is another type and is not so common. it involves two or more alleles are kept stable in a population; it is often resulted by heterozygous advantage and frequency-dependent selection.
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet Answers
- Question 1: A population of rabbits lives in a grassland environment. Some rabbits are white, some are brown, and some are gray. Over time, the grassland becomes increasingly rocky, with mostly white and dark gray rocks. Predict which type of selection might occur.
- Answer: Disruptive Selection. The extreme phenotypes (white and gray) are favored due to camouflage against the rocks, while the intermediate phenotype (brown) is selected against.
- Question 2: In a population of oak trees, the trees with average trunk thickness are more resistant to wind damage than trees with very thin or very thick trunks. What type of selection is likely taking place?
- Answer: Stabilizing Selection. The intermediate phenotype (average trunk thickness) is favored, reducing variation in trunk thickness.
- Question 3: A species of fish lives in a polluted lake. Initially, most fish are susceptible to the pollutant. However, over several generations, a higher percentage of the fish population becomes resistant to the pollutant. Which type of selection is at work?
- Answer: Directional Selection. The resistant phenotype is favored due to the presence of the pollutant, leading to a shift in the population’s resistance.
- Question 4: A moth species has two color forms: one is similar in color to tree bark and the other is similar to dried leaves. The moths with intermediate colors are easily seen by predators. What type of selection is occurring?
- Answer: Disruptive Selection. The extreme phenotypes (matching bark and leaves) are favored, while the intermediate phenotypes are selected against due to increased predation.
- Question 5: The birth weight in humans is around 7 pounds. Babies born significantly smaller or larger have higher mortality rates. What kind of natural selection is occurring?
- Answer: Stabilizing Selection. The intermediate phenotype (7-pound birth weight) is favored because it leads to higher survival rates.
If you are searching about Patterns Of Natural Selection Worksheet you’ve visit to the right web. We have 20 Pics about Patterns Of Natural Selection Worksheet like Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – Pro Worksheet, Natural Selection and Evidence Worksheet Worksheet for 9th – 12th and also Evolution By Natural Selection Worksheet Key – Printable PDF Template. Here you go:
Patterns Of Natural Selection Worksheet

learningschoolmiszegzy.z22.web.core.windows.net
Darwin Natural Selection Worksheet – Printable PDF Template

martinlindelof.com
Kami Export – Darwin's Natural Selection Worksheet 1 – Darwin’s Natural

www.studocu.com
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – Printable Word Searches

davida.davivienda.com
Charles Darwin And Natural Selection Worksheet

hitanjem74gglesson.z21.web.core.windows.net
12 Darwin's Natural Selection Worksheet Key – Free PDF At Worksheeto.com

www.worksheeto.com
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – E-streetlight.com
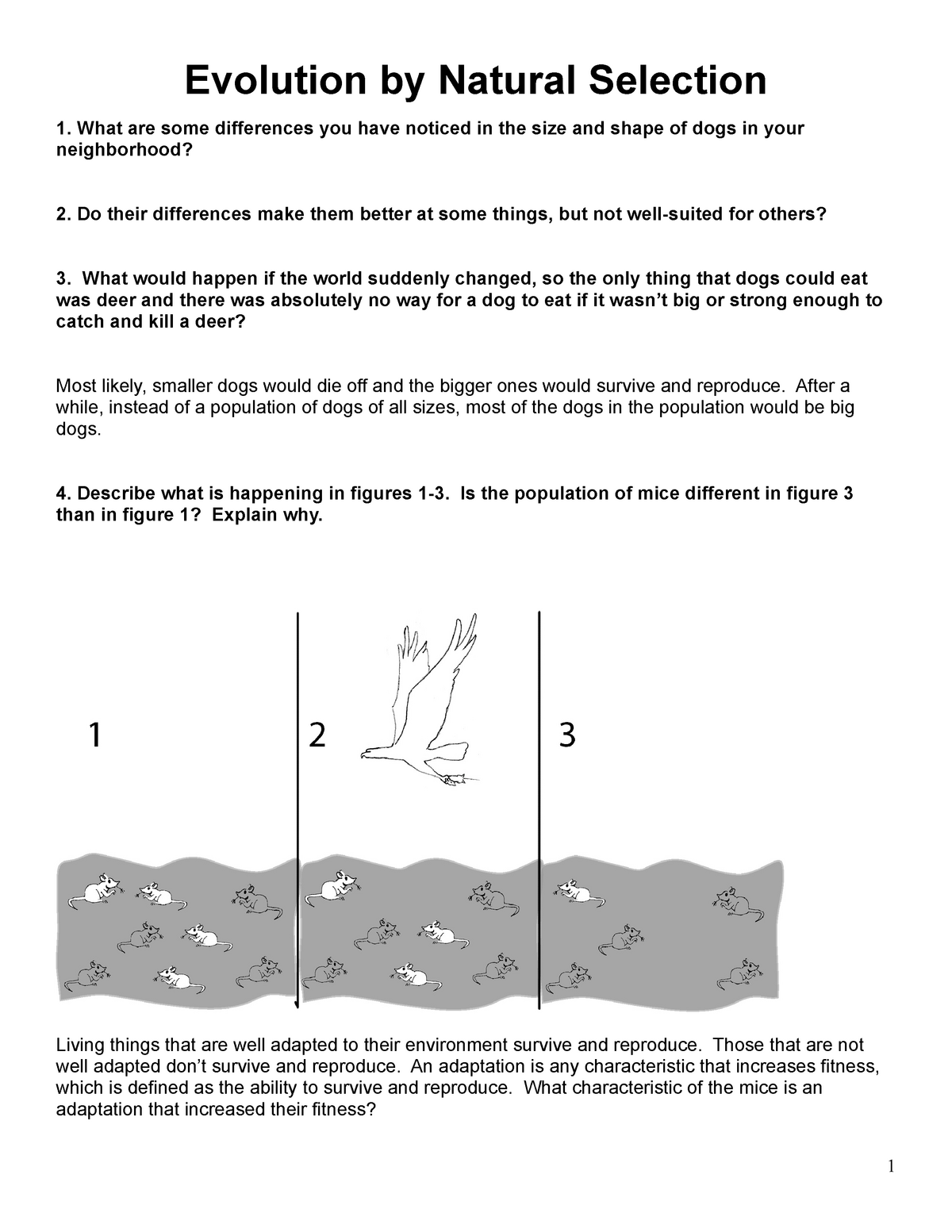
www.e-streetlight.com
Natural Selection | Cool.org

cool.org
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – Pro Worksheet

www.proworksheet.my.id
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – Pro Worksheet

www.proworksheet.my.id
Natural Selection And Evidence Worksheet Worksheet For 9th – 12th

worksheets.clipart-library.com
Natural Selection Worksheet For Middle School 24 – Printable PDF Template
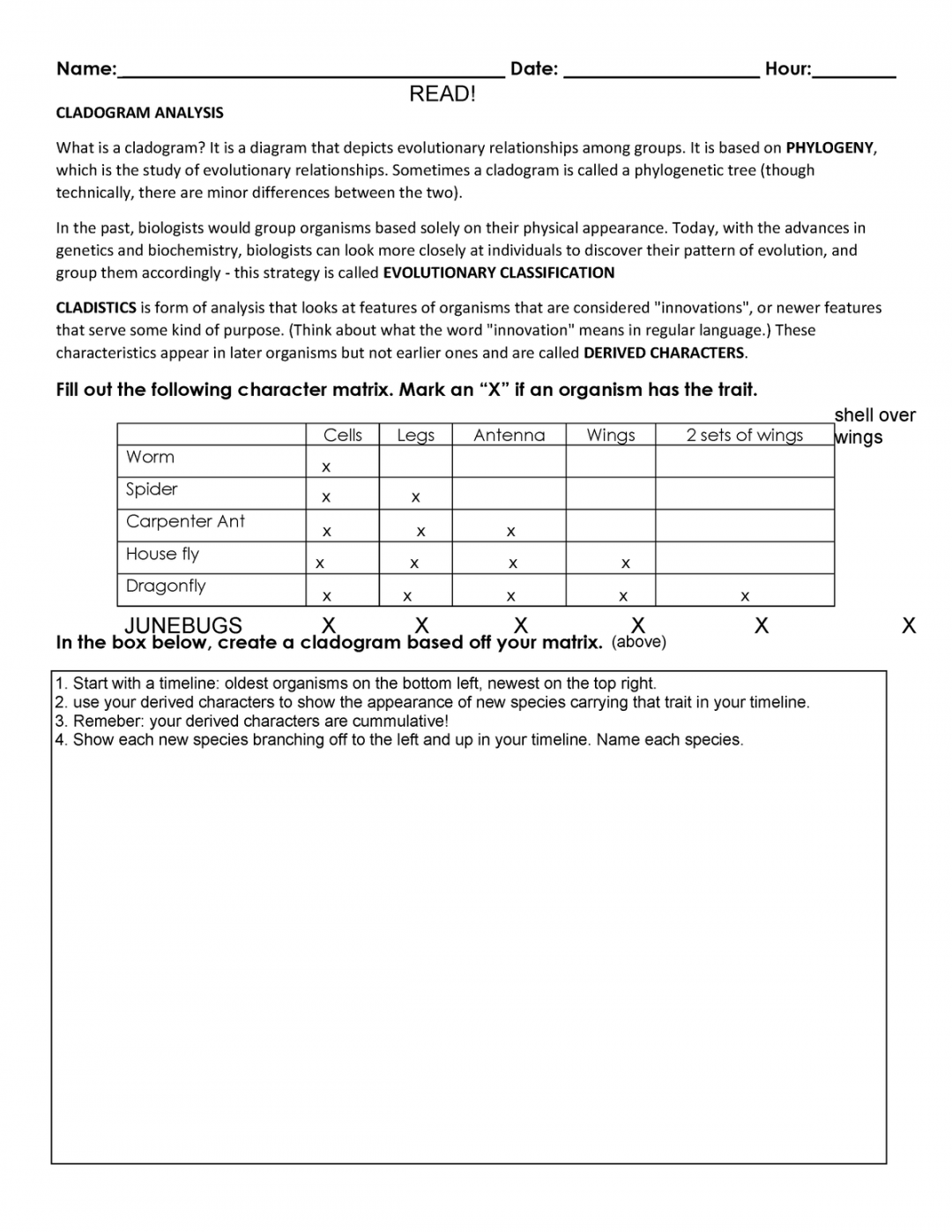
martinlindelof.com
3 Types Of Natural Selection Teach Pinterest Natural – Vrogue.co
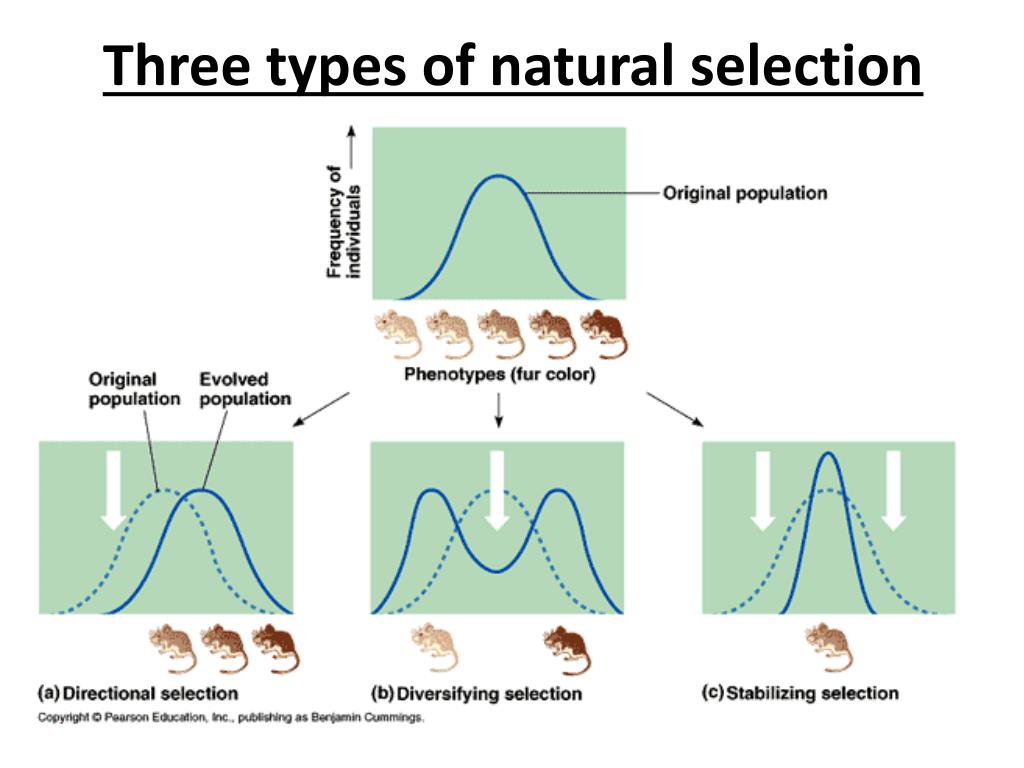
www.vrogue.co
Types Of Natural Selection Worksheet – Pro Worksheet

www.proworksheet.my.id
Natural Selection Worksheet For Middle School 1 – Printable PDF Template

martinlindelof.com
12 Darwin's Natural Selection Worksheet Key – Free PDF At Worksheeto.com

www.worksheeto.com
Darwin Natural Selection Worksheet – Printable And Enjoyable Learning

newark2.remotepc.com
Evolution By Natural Selection Worksheet Key – Printable PDF Template

martinlindelof.com
SOLUTION: Natural Selection Worksheet 1 – Studypool

www.studypool.com
Natural Selection Worksheet – Solutions – Name SOLUTIONS Worksheet

www.studocu.com
Types of natural selection worksheet – pro worksheet. Natural selection worksheet for middle school 24 – printable pdf template. types of natural selection worksheet – pro worksheet